As a computer user, we completely realize that multiple users can use a single machine as per their requirements. These users generally create separate user accounts to which they logged in whenever they want to access that computer system. In any operating system, whenever an issue arises during the execution of any process, the most important concept is accountability which can only be achieved if you can attribute an action to the actual doer. It means that if an error has occurred just now, then there is a very high chance that the user who is currently using the computer system has somehow caused this issue to occur. Also, if a system administrator wishes to make any changes to the configuration files within the system, then before doing that, he needs to make sure that no user is currently logged into the system so that he cannot cause any hindrance in the system configuration.
All these scenarios point to one common goal and that is to look out for how you can find out the currently logged in users of a system. So, in today’s article, we will be explaining to you all the different methods of printing the user names of the users currently logged into the Linux system on the terminal.
Note: Linux Mint 20 has been used to demonstrate all the methods of printing the user names of users currently logged into the Linux system.
Methods of Printing the User Names of Users Currently Logged into the Linux System:
There are several methods of printing the user names of users currently logged into the Linux system which are listed below:
Method # 1: Using the “who” Command:
The “who” command in Linux Mint 20 can be used to print the user names of the users currently logged into the system by running it in the following manner:
![]()
Running this command will not only display the names of the currently logged in users but it also displays the exact time at which the current user logged in as shown in the image below:
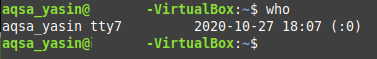
Method # 2: Using the “whoami” Command:
The “whoami” command in Linux Mint 20 can be used to print the user names of the users currently logged into the system by running it in the following manner:
![]()
The output of this command differs from the simple “who” command as it only displays the name of the currently logged in user and not any other details related to it like the time at which he logged in as you can see from the image shown below:
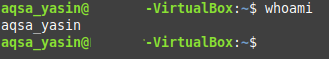
Method # 3: Using the “w” command:
The “w” command in Linux Mint 20 can be used to print the user names of the users currently logged into the system by running it in the following manner:
![]()
This command also displays the processes that the currently logged in user is running along with his name and also some other system related details as shown in the image below:
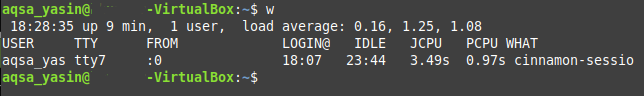
Method # 4: Using the “last” Command:
The “last” command in Linux Mint 20 can be used to print the user names of the users currently logged into the system by running it in the following manner:
![]()
Basically, this command fetches all the users that have ever logged in and out of the system from the time the /var/log/wtmp file has been created on your system. Out of all those users, the currently logged in user will be the very first user in the output. Also, along with the name of that user, the “no logout” status will be explicitly mentioned which will indicate that it is the name of the currently logged in user as shown in the image below:
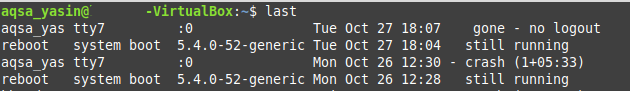
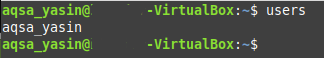
Method # 5: Using the “users” Command:
The “users” command in Linux Mint 20 can be used to print the user names of the users currently logged into the system by running it in the following manner:
![]()
The output of this command is exactly like the output of the “whoami” command i.e. it only displays the name of the currently logged in user as shown in the image below:
Method # 6: Using the “finger” Command:
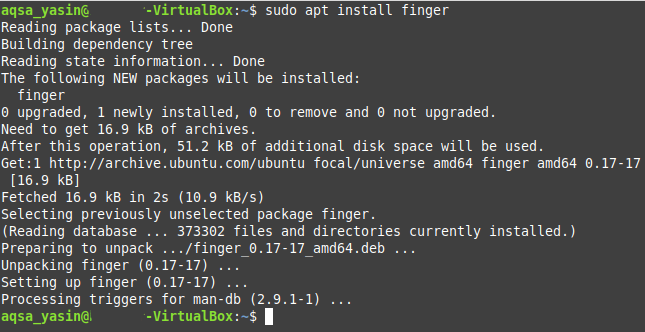
The “finger” command in Linux Mint 20 can be used to print the user names of the users currently logged into the system in the following manner:
First, you will need to install this command since it is not installed by default in your Linux Mint 20 system. To install the “finger” command in Linux Mint 20, the command stated below should be executed in the terminal:
![]()
This command will take a few seconds to execute successfully after which the “finger” command would be installed on your Linux Mint 20 system as shown in the image below:
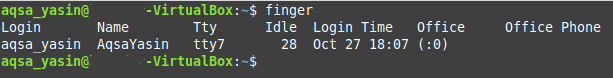
Now you can easily use the “finger” command to print the user names of the users currently logged into the system by running it in the following manner:
![]()
The output of the “finger” command is very much like the output of the “w” command except that the “Office” and “Office Phone” fields are new in the “finger” command as shown in the image below:
Conclusion:
In today’s article, we shared with you six different methods of printing the user names of users currently logged into the Linux system. In the end, we would like to provide you with a summary of all the methods discussed above so that you can quickly choose one according to your requirements. If you only wish to print the user names of the currently logged in users, then you can either use Method # 2 or Method # 5. If you also want to check the login time along with the user name, then you can use Method # 1. If you want to see some system-related details along with the currently logged in user names, then you can either use Method # 3 or Method # 6. Finally, if you want to check the user names of all the users who have ever logged into your system, then you can use Method # 4.
from Linux Hint https://ift.tt/32ftzVq




0 Comments