This article shows you how to use the built-in Google Chrome task manager on your system.
Google Chrome Task Manager
To open the Google Chrome Task Manager, click on the three dots icon in the top right-hand corner, then move your cursor to the ‘More tools’ option. A drop list with more options will appear, from which you will select ‘Task Manager.’ You can also open the Task Manager through keyboard shortcut keys. Press Shift + Esc for Windows and Search + Esc on OS Chrome.
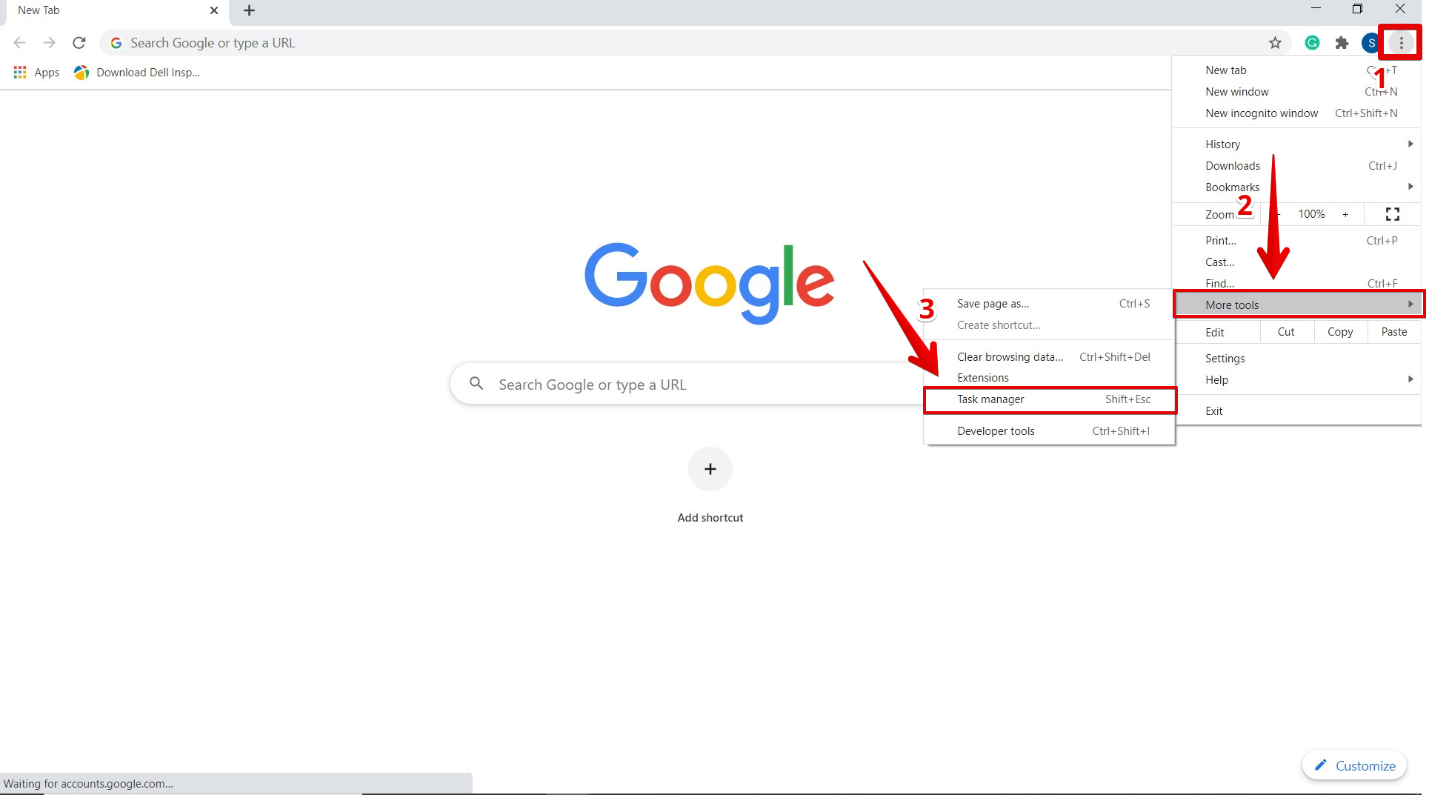
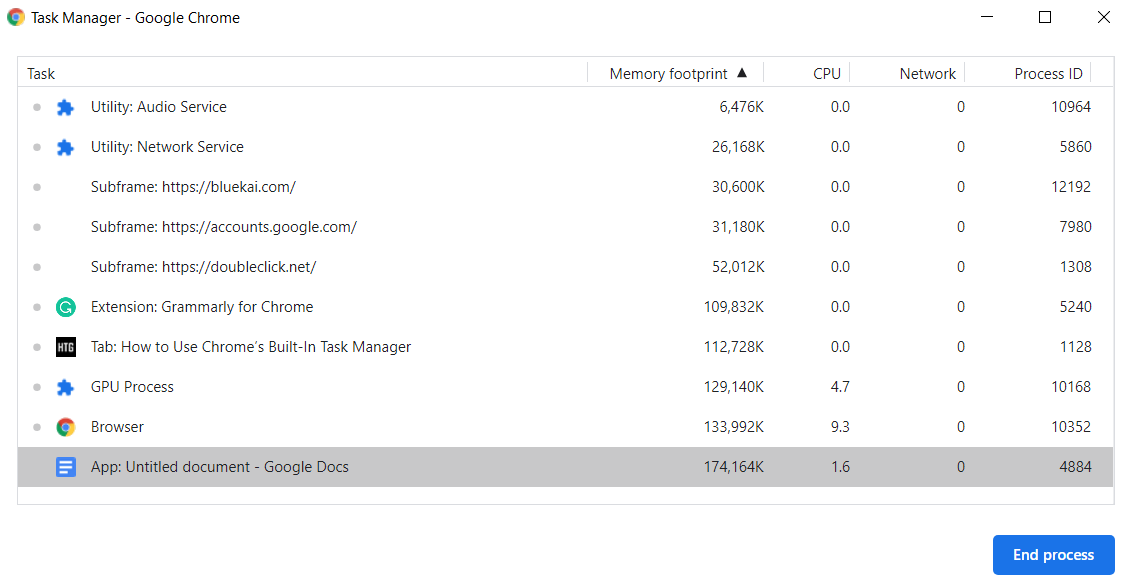
After clicking ‘Task Manager,’ the following window will appear, with a list showing all extensions, tabs, and currently running processes.

Terminate Not Responding Processes
You can terminate any process from the Task Manager Menu list. This can be useful when a tab or extension stops responding to the system. To perform this action, click on the process to select it and click ‘End Process’ to terminate the process. For example, if the data searching tab is not responding to you at any time, then you can easily stop this task upon selection.
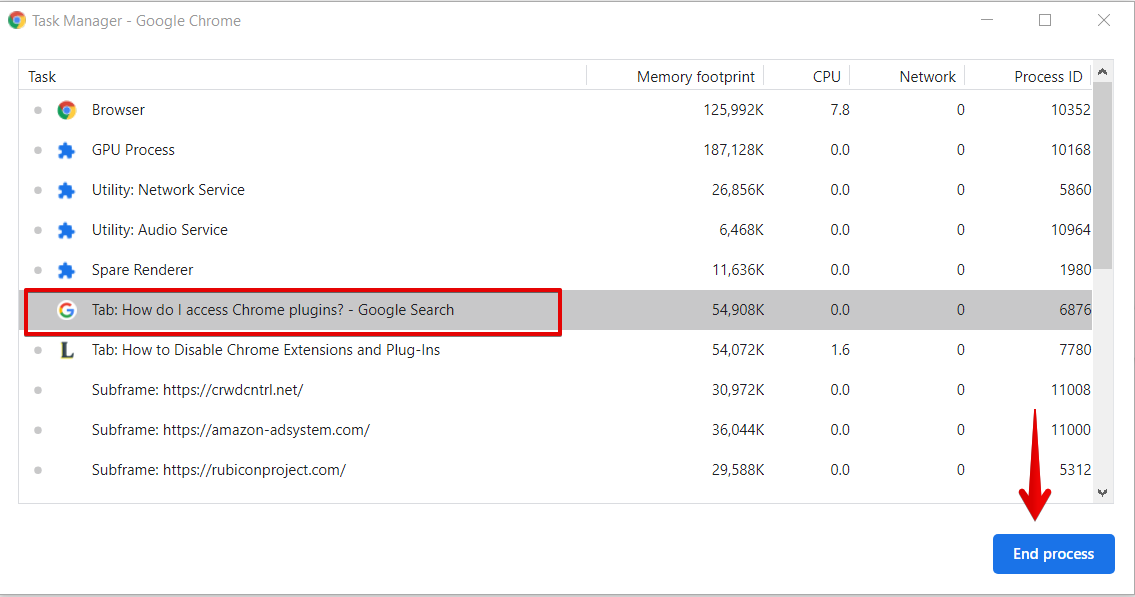
You can also terminate or kill several processes at once. To do so, for Windows, hold down the Shift or Ctrl key, and for Mac, highlight multiple processes from the list. After highlighting the selections, click the ‘End Process’ button. All the processes that you selected from the list will be terminated.

View All Available Resources for Running Tasks
Google Chrome has over 20 different categories of stats which you can add in the Task Manager Columns menu. You can easily look at the resources that all the processes are using. To do this, right-click on the particular process, and you will see a list of the context menu stats.
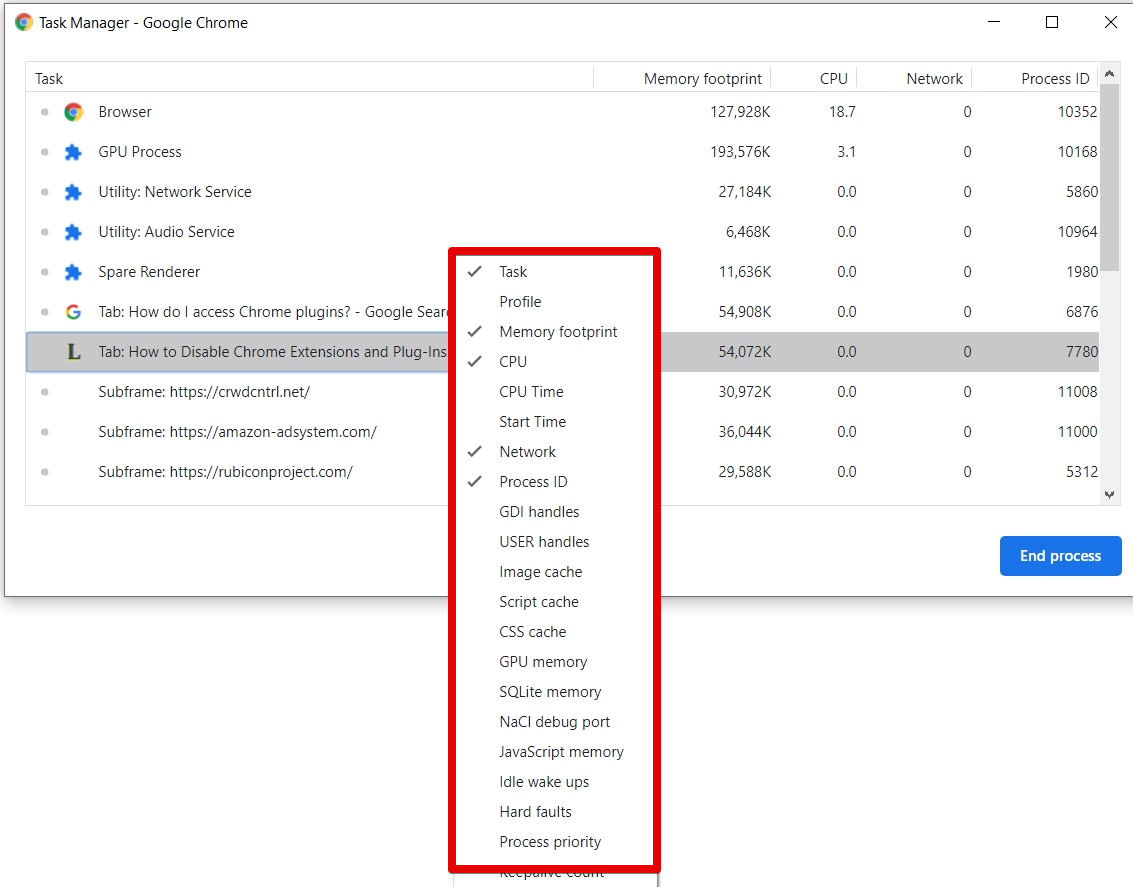
To add other resource categories in the Task Manager Columns, add a checkmark to each category you wish to add. Categories that already have a checkmark are displayed in the columns. To remove a category from the column list, remove the checkmark on that category.
For example, if you want to see the stats of the CPU time of each process in the column list, then you will checkmark this category.
You can also sort specific column stats by clicking on a column heading. For example, to sort memory footprint stats, click on the heading of the memory footprint column, and the process containing the most memory will be sorted and displayed at the top of the list.
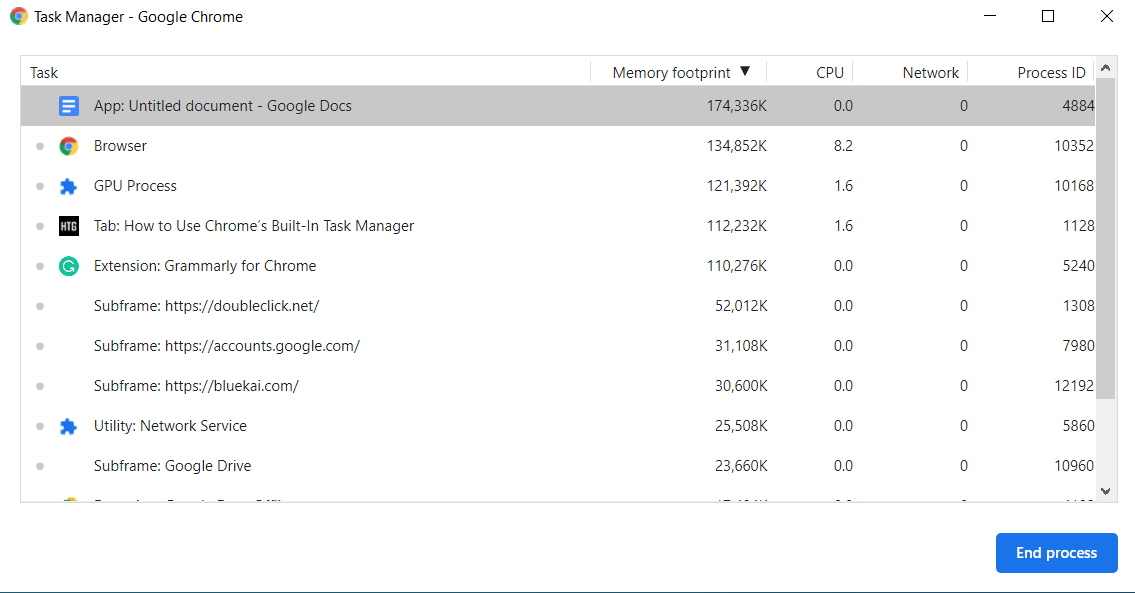
Similarly, to sort the process containing the least amount of memory, sort the list according to the memory footprint.
Conclusion
This article explained how to use the Google Chrome Task Manager. With this tool, you can monitor all running processes and stop processes that are not responding. In case of any query related to this article, please let us know via feedback.
from Linux Hint https://ift.tt/2EHr7hH




0 Comments