Redis String Data Type
Redis is an in-memory data store that supports more complex data structures when compared to other key-value data stores. Among all these complex data structures like sets, hashes, bitmaps, and lists, it supports the most uncomplicated string types as well. In that case, a string key maps to a string value. Usually, the SET and GET commands are used to create and fetch key-value data from the Redis store. Furthermore, the SET command creates a new key in the memory and maps a string value to it, nothing more than that. It will overwrite the value if the key already exists.
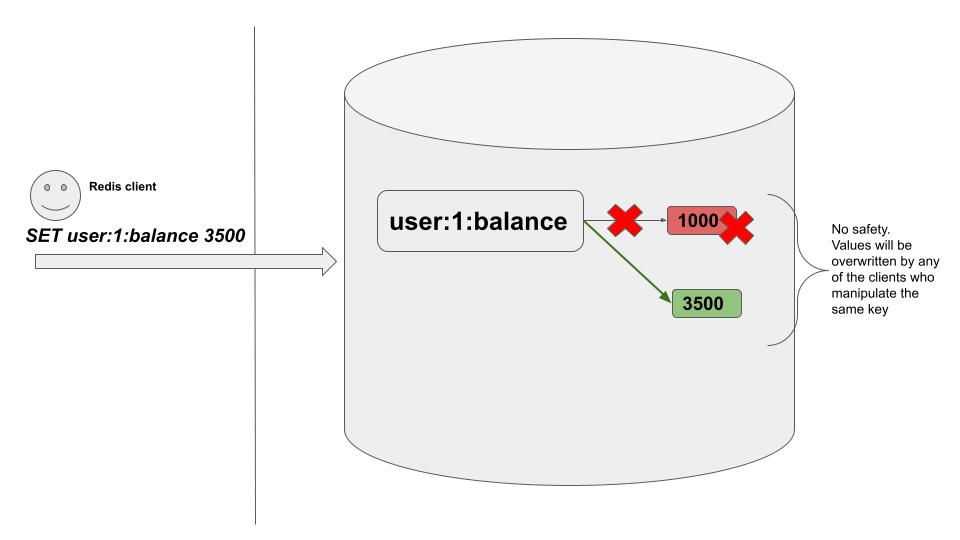
No safety mechanism is implemented with the SET command by default to handle the value mutations by multiple clients simultaneously without mutual agreement. This command has to be called with safety measurements in place, such as a locking mechanism.
Setting a Key Value Conditionally
It is always better to follow a safety measure when mutating a value that is stored at a given key. Hence, Redis has introduced an option to the SET command NX that is in place and will not mutate the value of an already existing key. The same behavior has been implemented with a new command which is explained in the next section.
The SETNX Command
The SETNX command, as its name suggests, “set if not exists,” which means the command will only set a value if and only if the specified key doesn’t exist in the data store. Whenever the specified key already exists, the command will not perform any operation on that key. With that restriction, the SETNX command is safer than the SET command. Furthermore, this command has constant time complexity.
Syntax:
SETNX redis_key value
redis_key: The unique identifier of a Redis key-value pair entry.
value: The value associated with the Redis key.
This command will return an integer reply where the 1 means key has been set with a new value. If the returned value is 0, the key is not set, and the existing key will hold the old value.
Example 01 – Locking Mechanism With SETNX
Let’s assume an online game where multiple players will access a common gold bucket owned by their team. Players can access the gold bucket and fill it up with the gold that they’ve found by exploring the world. Imagine player one accesses the gold bucket and drops some gold within a fixed period. At the same time, player two tries to consume some gold from the same bucket. In that case, the access shouldn’t be handed over to player two until player one releases the gold bucket. This can be implemented with the SETNX command with a simple locking mechanism.
The player:1 can use the SETNX command to set the total gold amount in the bucket. Let’s assume that we are going to store the gold amount in the key goldbucket.
As expected, the goldbucket key has been created with a value of 100. Now, player:1 has the lock. Let’s say player:2 is going to call the SETNX command to set the new gold amount.
This time the command returns 0 because the key goldbucket exists. In other words, the key is locked by the player:1 already. Hence, player:2 has to wait until player:1 releases the lock by deleting or automatic timeout expiration.
Let’s check the value associated with the goldbucket key, as shown in the following.
As expected, the value is still 100, which means the player:1 has already locked the data value. Hence, player:2 needs to keep waiting until the timeout expires and player:1 releases it.
There can be a deadlock situation if the client crashes or fails due to a network failure and the lock hasn’t been released by the crashed client. Multiple clients might notice this and try to remove the lock using the DEL command. As a result, each client will delete their own keys repeatedly, which will lead to a deadlock.
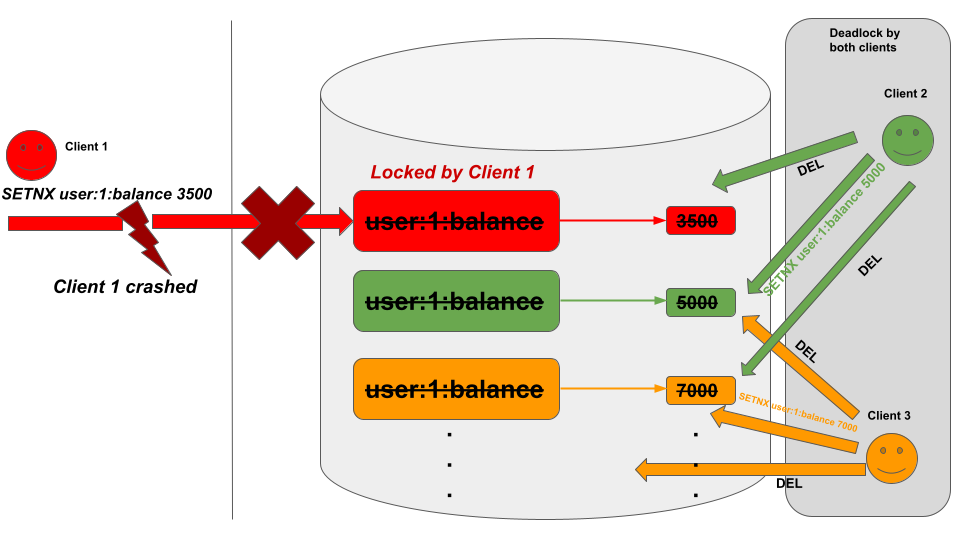
It can be resolved by each client checking for the timestamp in advance using the GETSET command and then acquiring the lock using the SETNX command if and only if the timestamp is expired.
Conclusion
To summarize, Redis is a key-value store that supports the simplest string data types among the other complex data structures like hashes, sets, bitmaps, and lists. As you all know, SET and GET are the most basic commands that can be used to create and fetch Redis key-value pairs. The SET method is used to create key-value pairs in the Redis database that eventually overwrites the associated value for a specified key if the key already exists in the database. As previously highlighted in the article, this unsafe value mutation can be restricted with the Redis SETNX command. The SETNX command sets the value for a given key if the key doesn’t already exist. Whenever a key exists, the command doesn’t perform anything and returns 0. Hence, the SETNX command is used to implement locking mechanisms in real-time applications.
from https://ift.tt/gb6HWlj




0 Comments