Example 1
To start a program for the hashset in C sharp, we will use two libraries in the source code. One is the system and the second one is the system.collections. Generic, these both header files play an important role in using classes and built-in functions to the program.
Using System.Collections.Generic;
Method 1:
Inside the class, the main program is declared. To create a hashset, we use a hashset class that is present in the collection library. A new hashset is created by using a new keyword, as it is involved in the dynamic creation of the hashset. A hashset is a string variable, as it contains all types of symbols, alphanumeric values, etc. After the hashset keyword, the name for the hashset is defined.
Once the hashset is created, we will now start adding items to the hashset one after another. This addition is done manually. The main built-in function used to enter values is the ‘add()’ function of C #. This function is called by the name of a new hashset that acts as an object. The value that is to be entered in the hashset is used as an argument in the parameter of the add function.
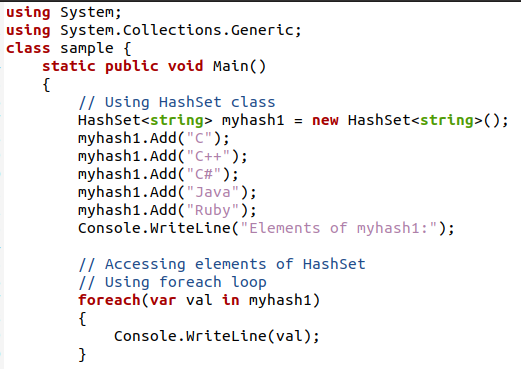
We have entered 5 values to the hashset by using the same add(). The add function acts like an append() function of the string that keeps on adding the values at the end of the string. After adding values, we will display them. To access elements in a hashset, we will use a Foreach loop. This loop will iterate till the last element of the hashset.
Method 2:
Another way of creating a hashset is to create it by using a collection initializer that initializes the Hashset. This is different from method 1, as we need to use an add() function to add items. But by using this initializer, we can add values at the time of declaring and creating the hashset.
Here the hashset is of integer data type. 5 integer values are entered into the function when the creation was done dynamically.
To display the elements in this hashset, we again use a Foreach loop so that it can access the last element of the hashset.

Save the code, and this will be executed in the terminal through the MCS compiler and a Mono that is used for the execution.
$ mono file.exe
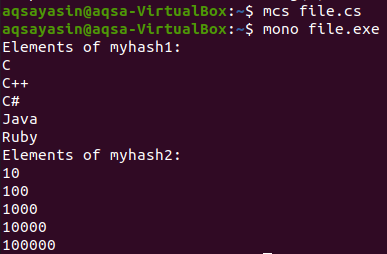
You can see that by using a Foreach loop, each item of the hashset is displayed.
Example 2
After adding elements, these items and the hashset can be modified by removing them or adding new items in the hashset. Now we will write a simple program to remove items from the hashset.
So first of all, we will again create a new hashset, as we did before by using the hashset class, and by using the add() method, all the elements will be added.

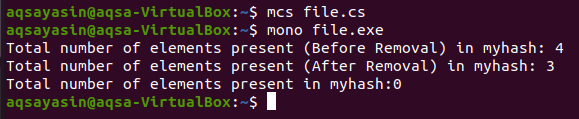
Before the removal of any item, we will like to display the number of items already present in the hashset. This will be done through a counter function. This count() function will be called through the hashset object.

After all the items are displayed once, we will now remove the item from the hashset by using a remove function.
In the parameter of the remove function, we pass the item that we want to remove. After removal, again, the count function will count the elements left after removing an item. Likewise, we can remove more items. But if someone wants to get the whole hashset empty, this is done by using a clear() function. This is used to remove all elements from the hashset. It is also called the hashset object.
Then we will check if the hashset is empty or not by counting the items through the count() function.
Example 3
Now working on the set operations, the hashset class contains some methods that are used to apply some operations on the hashset. One of them is a UnionWith. This operation is used to modify the current hashset by adding all-new items to it. All new items are appended with the previous one. But to keep integrity, the duplicate items are removed. For example, while adding elements simply to a hashset, if a hashset already has C sharp, but we again add the item C sharp, then this will be added to the current items. But by using the union operation, duplicity is removed; if an item is to be added if it already exists, then it will appear a single time; this is union. This is elaborated in an example.
First, we will create a hashset and then add a few items to it. After that, again, create another hashset through a hashset class, and then add an item to it through add() function. Adding items should be followed in such a way that some items should be the same as we have entered in the hashset. Now both the hashset contains all the items separately. We will join them through a specified function.
Now we will apply a UnioWith() method so that we can remove the copied items that occur twice in the hashset at the time of Union. This function is called through the object of the first hashset, and then the parameter will take the object of the second hashset.
By using it, all the items are present in the first hashset. Then we will print the values from the first hashset.

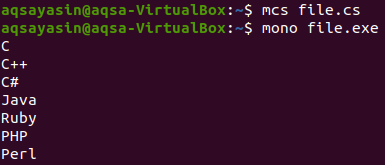
Contrary to UnionWith(), there is another operator that is used to get those items that are copied. In other words, those items from the hashset are selected that appear twice in the hashset. So to implement this, we will follow the same above example; we will create two hashsets and then add values to them. After that, we will apply the intersect function by using the objects of hashsets.

From the results, you can see that only two values were similar.
Conclusion
Hashsets can be created by using two approaches. One is from the hashset class that is defined in the header file library. And the second one is through the collection initializer. Both of them use different methodologies to add items in hashsets. We can also modify items once they are entered in hashsets. By using a hashset, it is easy to add or eliminate any item. Two basic operations are also mentioned here that are used to manage hashset items. We have explained all of these features of hashsets through elementary examples that are implemented in the Ubuntu operating system.
from https://ift.tt/HQ6hSzW




0 Comments