Using this short guide, you will understand how to format time in Golang using various formats and patterns.
The Basics
We use the Format() method and pass a Time object as the parameter to format time in go. The function syntax is as shown:
The function will return the time value formatted to the specified layout. You can define custom formats or use pre-defined ones. These include:
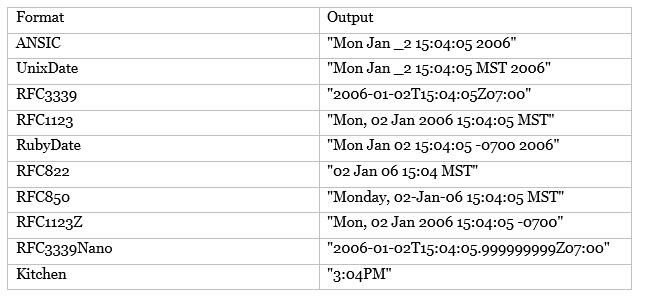
The layouts use the reference time on Mon Jan 2 15:04:05 MST 2006 to indicate the pattern under which to format the time object.
Example 1 – Custom Layouts
Let us look at a few examples of formatting time using various custom layouts.
current_time := time.Now()
fmt.Println(current_time.Format("2006-01-02"))
}
In the example above, we grab the current time using the time.Now() method. Next, we format the current time to YYYY-MM-DD using the reference date.
We can now execute the code above as shown:
2022-01-17
If we want to include the date and time in the 24-hr system, we can set the format as shown in the snippet below:
fmt.Println(current_time.Format("2006-01-02 15:04:05"))
The above code should return the output as:
To display the time in 12hr clock, we can do:
fmt.Println(current_time.Format("2006-01-02 3:4:5 pm"))
The code returns the output as:
Example 2 – Pre-Defined Layouts
You can also format according to a pre-defined layout by passing the layout as a string to the Format() Method.
Consider the following examples:
current_time := time.Now()
fmt.Println("ANSIC -> ", current_time.Format(time.ANSIC))
fmt.Println("UnixDate -> ", current_time.Format(time.UnixDate))
fmt.Println("Kitchen -> ", current_time.Format(time.Kitchen))
fmt.Println("RFC3339 -> ", current_time.Format(time.RFC3339))
fmt.Println("RubyDate -> ", current_time.Format(time.RubyDate))
fmt.Println("RFC822 -> ", current_time.Format(time.RFC822))
fmt.Println("RFC1123Z -> ", current_time.Format(time.RFC1123Z))
}
Once we run the above code, it should return the current time formatted into various pre-defined formats. An example output is as shown:
UnixDate -> Mon Jan 17 14:56:03 EAT 2022
Kitchen -> 2:56PM
RFC3339 -> 2022-01-17T14:56:03+03:00
RubyDate -> Mon Jan 17 14:56:03 +0300 2022
RFC822 -> 17 Jan 22 14:56 EAT
RFC1123Z -> Mon, 17 Jan 2022 14:56:03 +0300
Closing
This guide covers the basics of time formatting in the go programming language using the Format() method from the time package.
from https://ift.tt/nvN9fGT




0 Comments