The name suggests that it has a block and a chain. Yes, it is correct that a blockchain contains blocks and chains. Firstly, What is a blockchain, and what are these blocks and chains? A blockchain is a continuously added list of record records called blocks, which are linked together by the use of cryptography.
So, a blockchain network has a creator who builds and maintains the network, as well as members who join it. Members are all of the organizations that make up the network.
The history of blockchain
In his 1982 dissertation “Computer Systems Established, Maintained, and Trusted by Mutually Suspicious Groups,” cryptographer David Chaum presented a blockchain-like system for the first time. Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta presented more work on a cryptographically protected chain of blocks in 1991.
However, blockchain saw its use in 2009.
Satoshi Nakamoto created the first successful and popular implementation of Blockchain technology in 2009 by creating the first digital cryptocurrency called Bitcoin.
Features
- Consensus: For a transaction to be valid, all participants must agree on its validity.
- Decentralized: Means that no single person or organization controls the whole network. While everyone in the network has a copy of the distributed ledger, no one can change it on their own. It’s unique property allows openness and security while also providing consumers with control.
- Immutable: Immutability refers to the notion that any data which is published on the blockchain cannot be modified.
- Privacy: People place their faith in banks and financial organizations to store their money. Because transactions on a public blockchain are public, there is a need to investigate the possibilities of private blockchains for data-critical industries, as well as resolve challenges such as interoperability.
- Energy : The majority of currently operational blockchain networks are based on a proof-of-work mechanism. In which, network participants earns reward for solving the equation to add a new block to the network . This kind of computing power leaves massive carbon footprints that affect the environment.
Working
Let us now move on to the most exciting portion of the blog: how does it work? By now, we are aware that it is a decentralized network and distributed digital ledger idea. Legitimate and secure transactions can take place as a point-to-point exchange in this ledger system. So, let us look at how this technology works and how it is utilization to capture data and conduct secure transactions.
Blockchain is a network of several nodes or computers that works as a distributed network over the internet. Also, Each node is authorized to initiate a transaction, validate a transaction, receive a transaction, and produce a block. So, This is a cryptographically linked chain of blocks (sets of records) that cannot be falsified or modified. When we enter a series of transactions into a blockchain, it becomes a permanent part of it. Every node in it is the network has its own copy of the ledger or database. They may view the blockchain’s transaction history whenever they want, and it is updated every time a node adds a new batch of transactions (block) to the chain.
Understanding using an example
Step 1:
Assume that two nodes in a blockchain network, say node A and node B, desire to initiate a new transaction.
Step 2:
This transaction can only take place if all of the network’s other participant nodes confirm that it is a legal transaction. As a result, each node will get the request to validate the transaction between A and B.
Step 3:
Each node will verify specific aspects of the transaction, such as the validity of the two nodes, whether the transaction value is within limitations, whether A has enough funds to complete the transaction, and so on.
Step 4:
Once all of the nodes have checked and verified all of the aforementioned elements, the transaction is ready to proceed. The transaction is then added to a memory pool or mem pool.
Step 5:
A number of such validated transactions are pooled into mem pools, and numerous mem pools are combined to form a block. Each block has a certain amount of memory available for storing transactions.
Step 6:
Each new block will include a block header that includes a transaction data summary, a timestamp, the preceding block’s hash code, and its own hash. Every block has a unique hash code.
Step 7:
In order to add a new block to the existing blockchain, network nodes must do proof-of-work. Each block, as we know, has its own hash function.
Step 8:
A block is validated once a node completes its proof-of-work and solves the hash problem for that block. As additional nodes verify or complete the proof-of-work, it then adds to the blockchain. Each block contains its own set of transaction records. To add a new block in it, must include a fully unique collection of transactions.
Step 9:
Insertion of new block takes place. and a transaction between points A and B is completed. New blocks keep on adding indefinitely. There is a unique idea of incentives for performing proof-of-work that we will learn about in the next sessions.
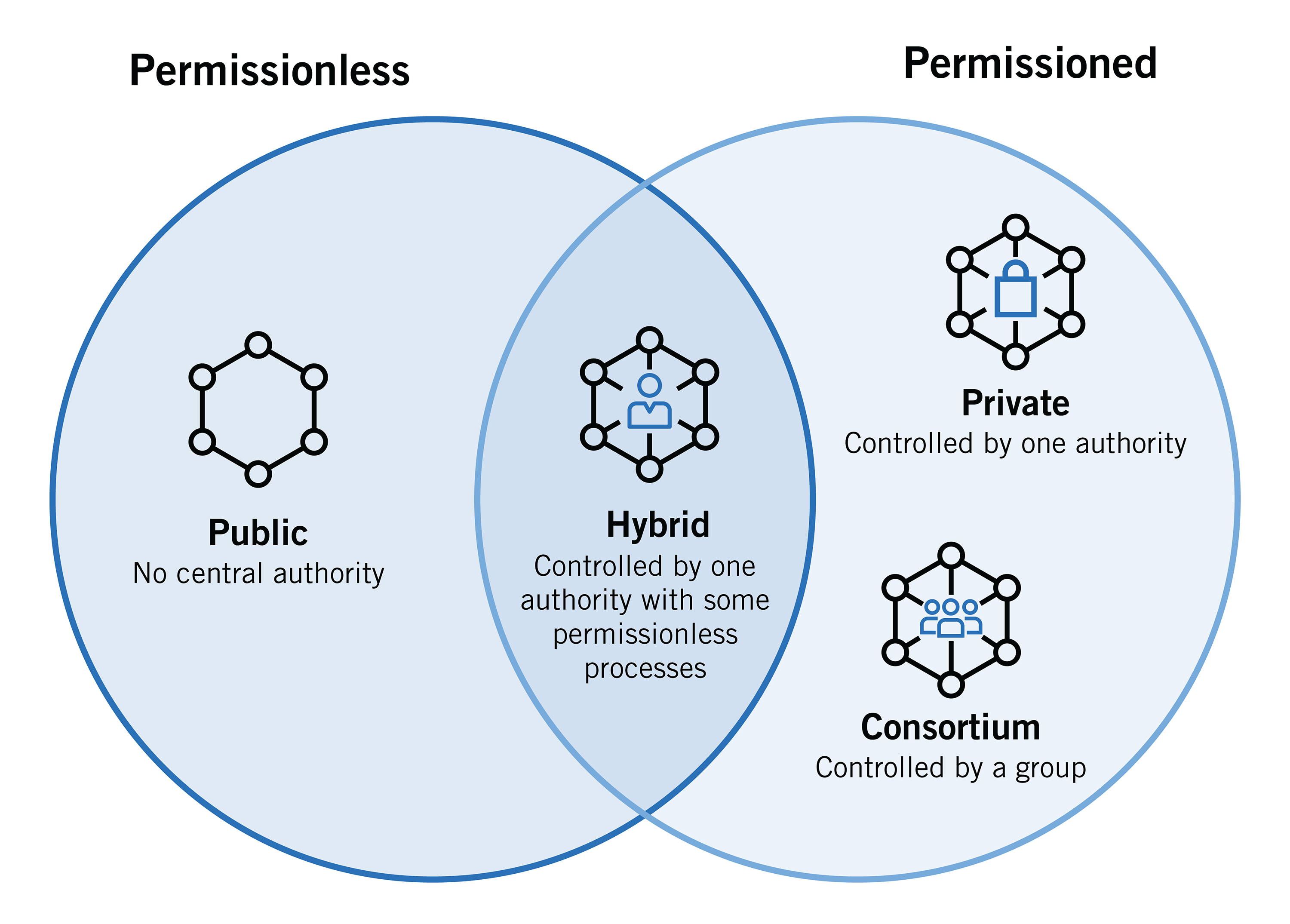
Types of blockchain
- Public Blockchain
It is a permissionless, non-restrictive distributed ledger technology. In this case, Anyone with an internet connection may join up for a blockchain platform and become an authorized node, becoming a member of the blockchain network. A node or user on the public blockchain has permission to view current and historical information, validate transactions, or perform proof-of-work for an incoming block, and mine. So, The most fundamental application of public blockchains is for cryptocurrency mining and exchange. As a result, the most popular public blockchains are Bitcoin and Litecoin blockchains. If users closely adhere to security rules and practices, public blockchains are largely safe. However, it is only dangerous when the participants do not strictly adhere to the security rules.Example: Cryptocurrency like bitcoin
- Private Blockchain
It is a restricted or permission blockchain. Generally, finds use in a close network. So, Private blockchain finds its use in an organization or industry where just a small amount of members participate in the network. The governing organization determines the degree of security, authorizations, permissions, and accessibility. As a result, private blockchains function similarly to public blockchains but have a smaller and more restricted network. Private blockchain networks find their use in voting, supply chain management, digital identity, asset ownership, and other applications.Example: cryptocurrencies like Monero, Dash, and Zcash.
- Hybrid Blockchain
It is one that combines private and public blockchains. It combines the properties of both types of blockchains, allowing for both a private permission-based system and a public permission-less one. Users may manage who has access to which data on the blockchain by using a hybrid network. However, The blockchain hybrid system is adaptable, allowing users to seamlessly connect a private blockchain to numerous public blockchains.For example the supply chain is the IBM food trust
- Consortium Blockchain
It is a semi-decentralized kind in which a blockchain network manages more than one entity. This contrasts with a private blockchain. In this sort of blockchain, more than one organization can operate as a node, exchanging information or mining. Banks, Government agencies, and other organizations often use Consortium blockchains
Example: Quorum and Corda
Application
It finds uses in the majority of cryptocurrencies to record transactions. For example, a famous cryptocurrency Bitcoin is based on blockchain.
Hospitals and vendors also utilize them for maintaining records of medical equipment. China uses this technology to speed up the time of payment of health insurance.
Blockchain technology, such as cryptocurrencies and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), comes into the picture to monetize video games. Many live-service games provide in-game customization choices like character skins or other in-game goods that players can acquire and exchange with other players using in-game cash.
Food Supply Chain monitoring is essential for tracing the origins of food. So, It assures that the eatables provided are safe to consume.
However, because of the way the food supply chain is currently structured, it is difficult for food manufacturers and merchants to authenticate its origin.
With the advent of blockchain technology, it is now feasible to instill confidence and transparency in the food supply chain ecosystem, assuring food safety for everybody.
Advantages of blockchain
The Blockchain format is designed in such a manner that it can readily discover and solve any problems. It also leaves a permanent audit trail. The design of this technology is
This technology is extremely safe since each user who joins the Blockchain network is assigned a unique identifier that is tied to his account.
Prior to the introduction of the blockchain, traditional banking organizations took a long time to process and initiate transactions, but with this technology, transaction speed rose dramatically.
Disadvantages of blockchain
The central government has established and controls contemporary money in every corner of the planet. So, It becomes difficult for Bitcoin to get acceptance by pre-existing financial institutions.
According to surveys, the average cost of a Bitcoin transaction is $75-$160, with the majority of this cost covered by energy usage. Finally, There are extremely few odds that we would be able to overcome this issue through technological growth.
from https://ift.tt/3tjJAYq




0 Comments