Example-1: Using for Loop to sort a dictionary
Create a python file with the following script to sort a dictionary using nested for loops. Two types of sorting have been shown in the script. A dictionary of four items has been declared here. The student’s name has been stored in the key, and the obtained mark has been stored in the value. An empty dictionary object has been declared before sorting to store the data of the sorted dictionary. After printing the original dictionary values, the nested ‘for’ loops have used to sort the dictionary based on the values by comparing the values of the dictionary. Another nested ‘for’ loop has used to sort the dictionary based on the keys by comparing the dictionary’s keys.
marks = {'Neha Ali': 83, 'Abir Hossain': 98, 'Jafar Iqbal': 79, 'Sakil Ahmed': 65}
# Print the original values of the dictionary
print("Original dictionary: \n", marks)
# Sort the values of the dictionary
sort_values = sorted(marks.values())
sorted_marks = {}
# Create the sorted dictionary based on values
for i in sort_values:
for k in marks.keys():
if marks[k] == i:
sorted_marks[k] = marks[k]
break
# Print the sorted dictionary
print("Sorted dictionary based on the values: \n", sorted_marks)
# Sort the keys of the dictionary
sort_keys = sorted(marks.keys())
sorted_keys = {}
# Create the sorted dictionary based on keys
for i in sort_keys:
for k in marks:
if k == i:
sorted_keys[i] = marks[k]
break
# Print the sorted dictionary
print("Sorted dictionary based on the keys: \n", sorted_keys)
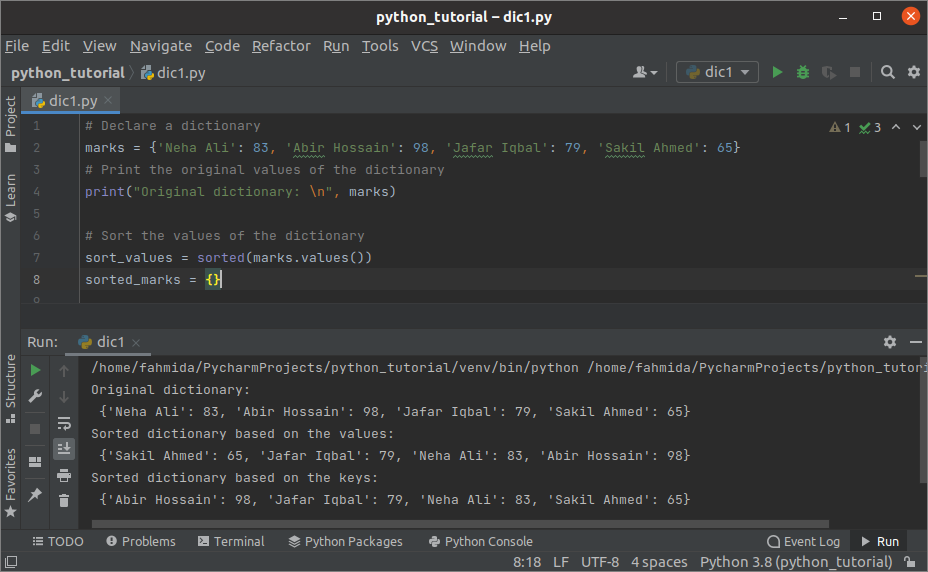
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above script. The original dictionary, the sorted dictionary based on the values, and the sorted dictionary based on the keys have shown in the output.
Example-2: Using sorted() function with lambda
Using sorted() function with lambda is another way to sort a dictionary. Create a python file with the following script to sort a dictionary using the sorted() function and the lambda. A dictionary of four items has been declared in the script. The sorting type can be set by using lambda. The index position has been set to 1 in the third argument of the sorted() function. That means the dictionary will be sorted based on the values.
marks = {'Neha Ali': 83, 'Abir Hossain': 98, 'Jafar Iqbal': 79, 'Sakil Ahmed': 65}
# Print the original values of the dictionary
print("Original dictionary: \n", marks)
# Sort the dictionary based on marks using lambda
sorted_marks = sorted(marks.items(), key=lambda x: x[1])
print("Sorted dictionary based on the marks: \n", sorted_marks)
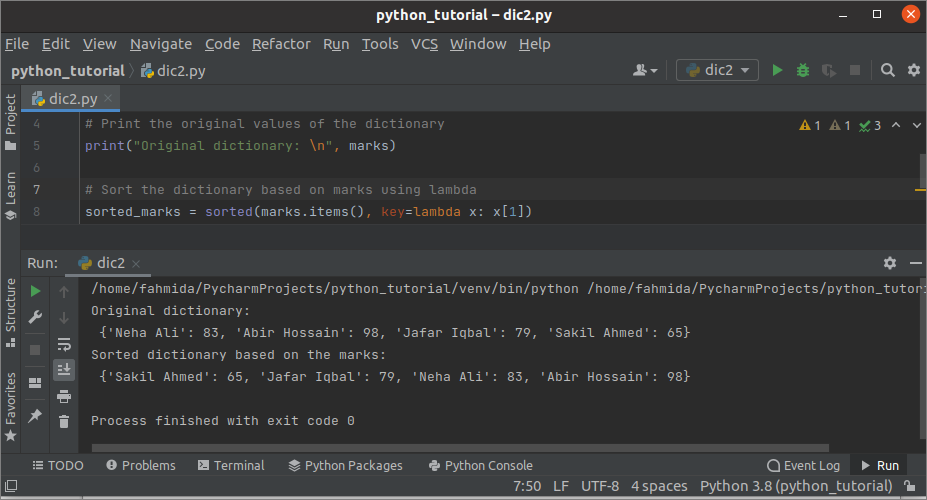
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above script. The original dictionary, the sorted dictionary based on the values have shown in the output.
Example-3: Using sorted() function with items()
Using sorted() function with items() function is another way to sort a dictionary, and it sorts the dictionary in ascending order based on keys by default. You can set the value of the reverse to True if you want the sorting in descending order. Create a python file with the following script to sort a dictionary using the sorted() function and the items(). The item() function is used to retrieve the keys or values from the dictionary. The sorted() function has used inside the dict() function to get a sorted dictionary as the output.
marks = {'Neha Ali': 83, 'Abir Hossain': 98, 'Jafar Iqbal': 79, 'Sakil Ahmed': 65}
# Print the original values of the dictionary
print("Original dictionary: \n", marks)
# Sort the dictionary based on names using dict() and sorted()
sorted_marks = dict(sorted((key, value) for (key, value) in marks.items()))
print("Sorted dictionary based on the names: \n", sorted_marks)
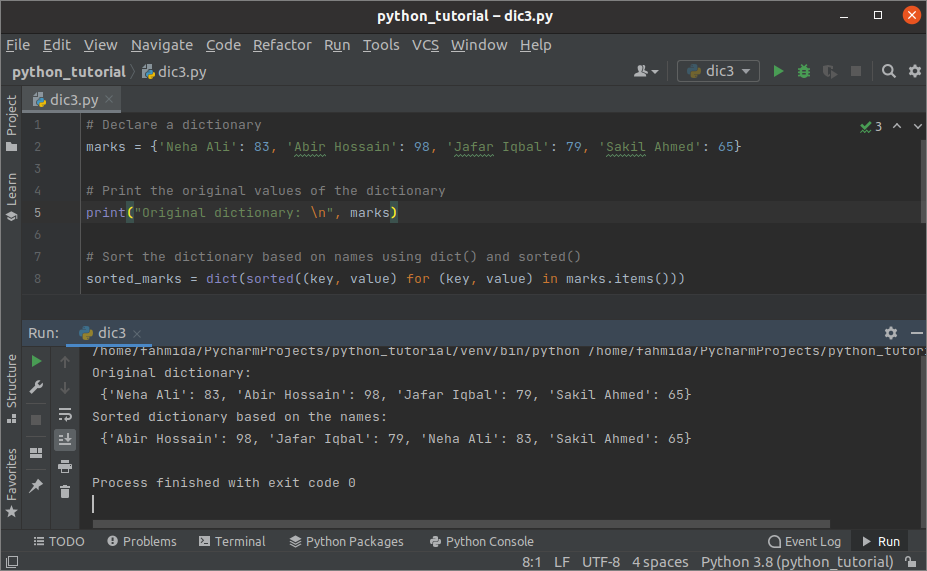
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above script. The original dictionary, the sorted dictionary based on the keys as shown in the output.
Example-4: Using sorted() function with itemgetter() function
Using sorted() function with itemgetter() function is another way to sort a dictionary. It also sorts the dictionary in ascending order by default. The itemgetter() function is under the operator module. Create a python file with the following script to sort a dictionary using the sorted() function and the itemgetter() function. You can set the sorting type using the itemgetter() function like the lambda. According to the following script, the dictionary will be sorted based on the values because 1 has passed as the argument value of the itemgetter() function.
import operator
# Declare a dictionary
marks = {'Neha Ali': 83, 'Abir Hossain': 98, 'Jafar Iqbal': 79, 'Sakil Ahmed': 65}
# Print the original values of the dictionary
print("Original dictionary: \n", marks)
# Sort the dictionary based on marks using itemgetter()
sorted_marks = sorted(marks.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1))
# Print the sorted dictionary
print("Sorted dictionary based on the marks: \n", dict(sorted_marks))
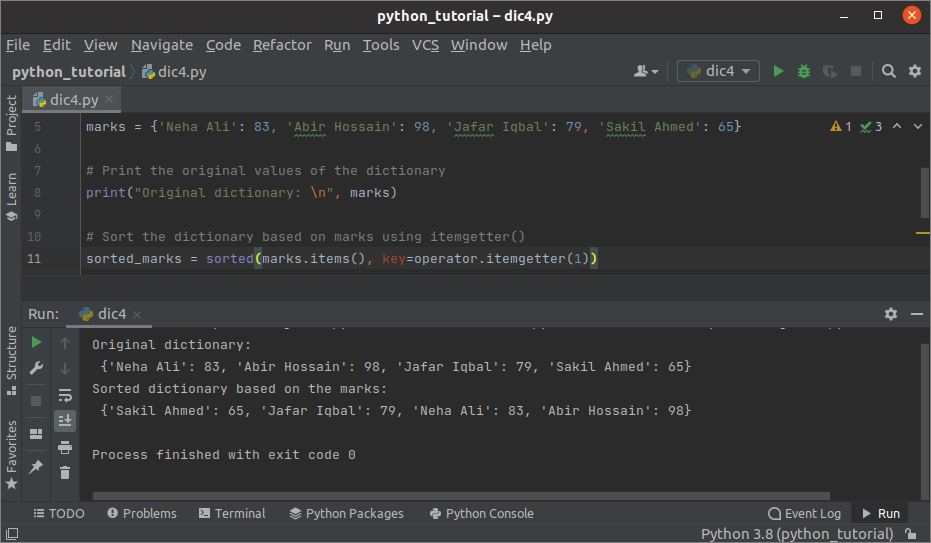
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above script. The original dictionary, the sorted dictionary based on the values have shown in the output.
Conclusion:
A dictionary can be sorted with or without using the built-in function of Python. Four different ways to sort a dictionary have been explained in this tutorial by using various types of functions. The sorted() function is the main function to sort a dictionary. The order of the sorting can also be set by this function. Another function or index is used to sort the data based on the keys or values by mentioning the argument or the index value.
from Linux Hint https://ift.tt/3eeZCuj




0 Comments