Files with the .CRT extensions are normally SSL/TLS certificates. The .CRT extension is one of the most commonly used SSL/TLS certificate formats in Linux and other Unix-like systems.
This tutorial will answer your question regarding creating a .CRT certificate file in Linux using the OpenSSL tool.
Prerequisites
- A Linux system
- A user with sudo privileges
Install OpenSSL
OpenSSL is an open-source that you can use to create self-signed SSL/TLS certificates with the .crt extension. You may already have the OpenSSL tool available on your Linux machine. Run the command below to confirm.
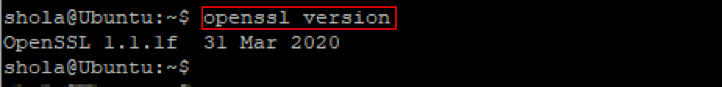
Figure 1: Check OpenSSL version
If OpenSSL is not already installed, then run the next command.
On Ubuntu/Debian based distributions:
On CentOS/Red Hat-based distributions:
The syntax for using the OpenSSL tool is:
Get a Private Key and a Certificate Signing Request File
Next, run the first command below to generate your private key. And the second command will output a certificate signing request (CSR) file.
$ openssl req -new -key private.key -out request.csr
Here’s a description of each command and option.
- genrsa Generate an RSA private key
- -out Output file
- -req Certificate signing request
- -new New request
- -key Path to a private key file
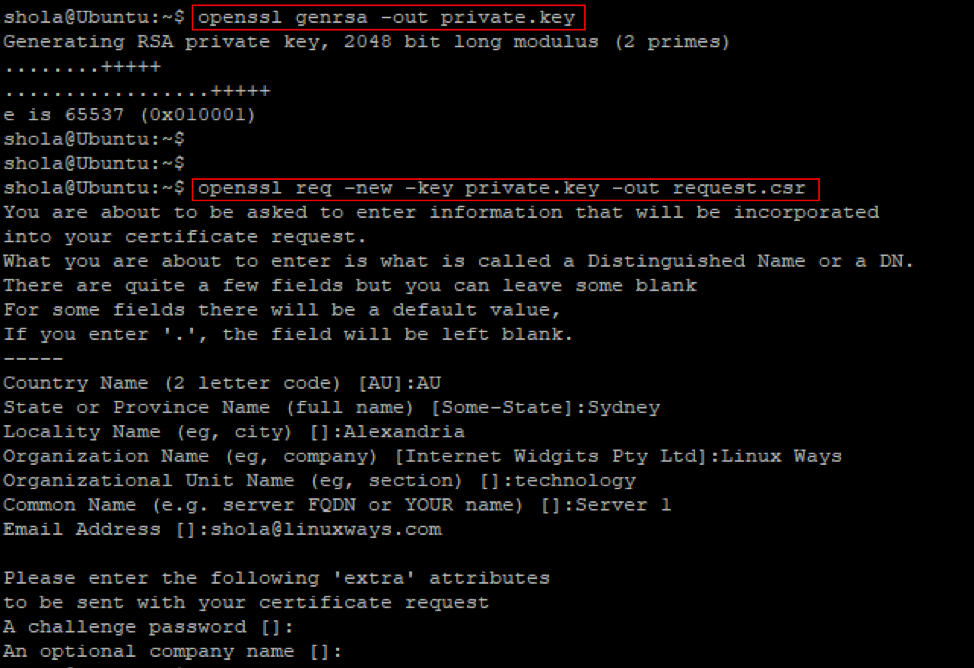
Figure 2: Private key and CSR file
You require your private key to sign the SSL/TLS certificate. The CSR file will hold information about the entity for creating the SSL/TLS certificate. You would be prompted to enter your information accordingly.
Note: While generating the CSR file, you may leave some fields blank by hitting enter on the keyboard. It is okay to leave the fields under ‘extra’ attributes blank.
Create a .CRT File
After the private key and CSR files are generated, it is time to create your .crt file.
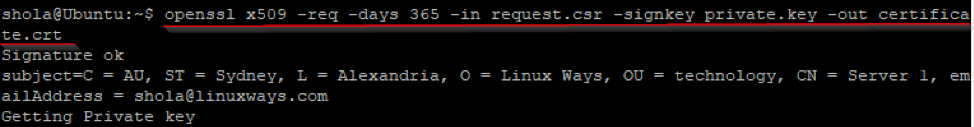
Figure 3: Generate .crt file with OpenSSL
Below is a description of each command and option.
- x509 Certificate data management standard
- -req Certificate signing request
- -days Number of days the certificate should be valid for
- -in Path to CSR file
- –signkey Path to private key file for signing the certificate
- -out Output file for the signed certificate
Your .CRT file will be saved in the current working directory, except you specified a different path.
Conclusion
Following this guide, you should now create a .CRT file by using the OpenSSL tool. Technically, this is a self-signed certificate and should be for internal use or testing and development purposes. Major web browsers do not have confidence in self-signed certificates.
from Linux Hint https://ift.tt/3dtyp6g




0 Comments