Whenever we run a Bash command on our Linux Mint 20 terminal, the regular practice is to see some output on the terminal. This is the same for the commands as well as for the Bash scripts. Sometimes, we may not wish to see that output. This happens especially when we want to debug a program and are only interested in finding out the errors that are occurring. In this situation, if we will be presented with the whole output, then it will not only be useless for us but will also waste our time looking for the actual issue.
That is why we prefer suppressing the actual output of the Bash commands or scripts in a way that only their errors (if any) are displayed on the terminal. Otherwise, nothing will be displayed. Therefore, today, we will be talking about the method of suppressing all output from Bash command in Linux Mint 20.
Method of Suppressing all Output from Bash Command in Linux Mint 20:
For explaining to you the method of suppressing all output from Bash command in Linux Mint 20, we would like to share some examples with you.
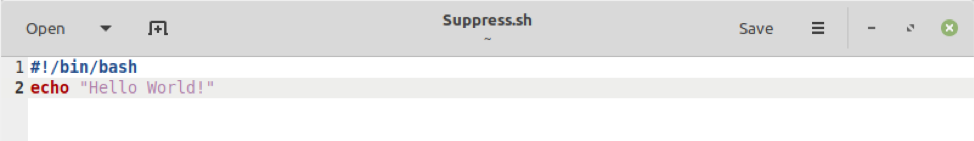
We have created a simple Bash script in which we are just printing a random message on the terminal. We will be using this Bash script in Example # 1 and Example # 2. This Bash script is displayed in the affixed image. We have named our Bash file as Suppress.sh.
Example # 1: Suppressing the Execution of a Bash Script/ Suppressing the Output of the “bash” Command:
The Bash script that we have just created can simply be executed with the “bash” command. Before suppressing the output of the “bash” command, we would first like to show you its actual output. For that, you need to execute your Bash script as follows:
![]()
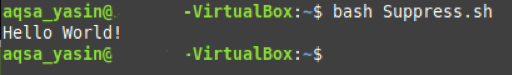
Executing this Bash script will simply display our dummy message on the terminal, as shown below:
Now, to suppress the output of the “bash” command, we will run the following command in our terminal:
![]()
Executing the above-cited command will send all the output to the >/dev/null bucket, and hence nothing will be displayed on your terminal as shown in the appended below image:

Example # 2: Suppressing the Output of the “cat” command:
We can also display the contents of our Bash script file on the terminal by using the “cat” command. Before suppressing the output of the “cat” command, we would first like to show you its actual output. For that, you need to run the “cat” command as follows:
![]()
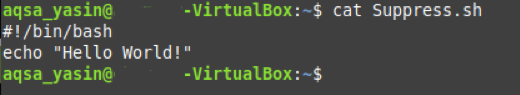
Executing the “cat” command will simply display the contents of our Bash script file on the terminal as shown below:
Now, to suppress the output of the “cat” command, we will run the following command in our terminal:
![]()
By executing the above-cited command will send all the output to the >/dev/null bucket, and hence nothing will be displayed on your terminal as shown in the appended below image:

Example # 3: Suppressing the Output of the “–help” command:
If you want to find out the details about the usage of any command or package in Linux Mint 20, you can make use of the “–help” command. Before suppressing the output of the “–help” command, we would first like to show you its actual output. For that, you need to run the “–help” command as follows:
![]()
We wanted to access the help manual of the nano editor, which is shown in the image below:

Now, to suppress the output of the “–help” command, we will run the following command in our terminal:
![]()
By executing the above-cited command will send all the output to the >/dev/null bucket, and hence nothing will be displayed on your terminal as shown in the image appended below image:

Example # 4: Suppressing the Output of the “–version” command:
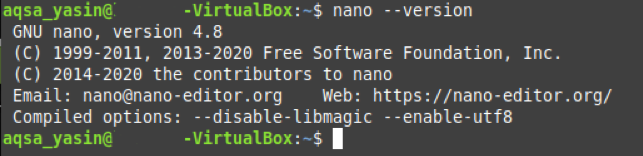
If you want to check the version of any installed package or command in Linux Mint 20, you can make use of the “–version” command. Before suppressing the output of the “–version” command, we would first like to show you its actual output. For that, you need to run the “–version” command as follows:
![]()
We wanted to check the version of the nano editor, which is shown in the image below:
Now, to suppress the output of the “–version” command, we will run the following command in our terminal:
![]()
By executing the above-cited command will send all the output to the >/dev/null bucket, and hence nothing will be displayed on your terminal as shown in the image appended below:

Example # 5: Suppressing the Output of the “man” command:
Whenever you want to read the manual or man pages of any installed command or package in Linux Mint 20, you can make use of the “man” command. Before suppressing the output of the “man” command, we would first like to show you its actual output. For that, you need to run the “man” command as follows:
![]()
We wanted to access the manual of the nano editor, which is shown in the image below:
Now, to suppress the output of the “man” command, we will run the following command in our terminal:
![]()
By executing the above-cited command will send all the output to the >/dev/null bucket, and hence nothing will be displayed on your terminal as shown in the below-appended image:

Conclusion:
In this article, we shared with you five different examples of suppressing all output from Bash command in Linux Mint 20. By going through these examples, now you will easily be able to suppress the output of any desired Bash command or Bash script while using Linux Mint 20.
from Linux Hint https://ift.tt/33NnXlR




0 Comments