The syntax of upper() function
The syntax of the upper() function is:
str.upper()
While using the upper() function, we just have to write the name of our string and call the upper() function. Let’s see the examples of upper() function.
Examples
Let’s declare a lowercase character string and convert it to the uppercase characters.
name = "kamran sattar awaisi"
#printing the original string
print("This is the original string:")
print(name)
#converting the string into uppercase
print("This is the converted string:")
print(name.upper())
Output
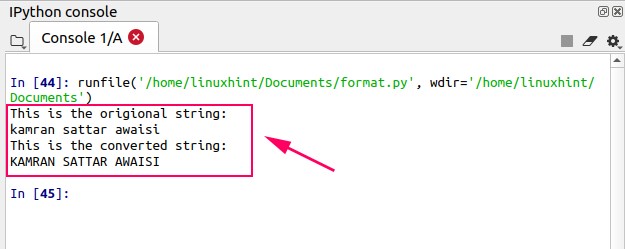
Now let’s declare a string that has few lowercase letters and few uppercase letters. The upper() function will convert the whole string into uppercase letters.
name = "LinuxHint is WEb BasEd Learning PoRtal"
#printing the original string
print("This is the original string:")
print(name)
#converting the string into uppercase
print("This is the converted string:")
print(name.upper())
Output
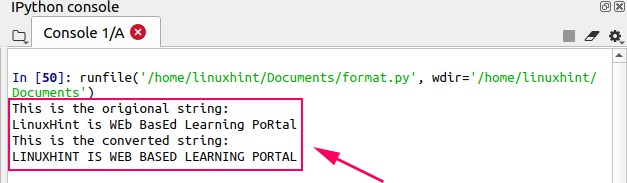
There are many applications of the upper() function. For example, Python is a case sensitive language. If we want to compare the two string, we can convert them into uppercase, and then we can compare them.
name_str1= "kamran sattar awaisi"
#declaring the second string
name_str2="KAMrAn saTTAR aWaiSI"
#converting the strings into uppercase and comparing them
if name_str1.upper()==name_str2.upper():
print("Both the strings are same")
else:
print("The strings are not same")
Output
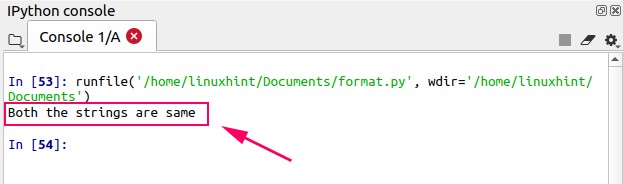
Conclusion
The upper() function is used to convert the string uppercase characters. This article explains the use of the upper() function with the help of simple examples.
from Linux Hint https://ift.tt/35i1CN9




0 Comments