We cannot access a variable if it is outside the scope of the function, and so the variables we want to use must have the proper scope upon declaration. To avoid issues related to scope, it is important to understand global variables. Therefore, in this article, we are going to discuss global variables and scope.
The scope of a function can be considered as a boundary within which the function can be accessed. However, while a function does not know what is happening beyond the curly brackets that define it, a global variable can be accessed from anywhere in the program.
Syntax
The syntax used to create a global variable, shown below, is no different than that used to create other variables.
However, the location of this declaration is very important. We will explore this concept more fully by considering some examples.
Example
First, let’s create a function called subtraction.
var subNum = 23;
}
In this function, we initialized a variable and assigned it a value. Now, we can try to access the variable in another function, i.e., division, and call that function.
console.log(subNum);
}
division();
However, we get the following reference error because the variable subName is not defined within the correct scope.

This error will occur any time we try to access subNum outside the function in which it is defined. For example:
var subNum = 23;
};
console.log(subNum);
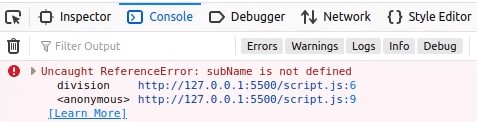
Here, we still cannot access the variable because it is restricted to the subtraction function.
However, let’s see what happens if we create the variable outside the function—for example, at the beginning of the script:
Now, let’s try to access it:
As shown below, we no longer get a reference error.
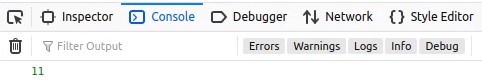
Furthermore, globalVar should be accessible from any function.
console.log(globalVar);
}
division();
As you can see below, globalVar is still accessible.
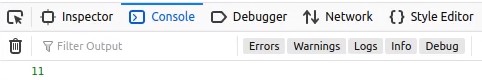
Conclusion
In this article, we explained scope and global variables by using simple examples. We hope you continue learning JavaScript with linuxhint.com.
from Linux Hint https://ift.tt/3dIsf1A




0 Comments