A module is typically used to divide the large functionality into small manageable files. We can implement our most used functions in a separate module, and later on, we can call and use it everywhere. The module’s creation promotes reusability and saves a lot of time.
Create Python modules
To create a Python module, open a Python script, write some statements and functions, and save it with .py extension. Later on, we can call and use these modules anywhere in our program.
Let’s create a new module named “MathOperations”. This module contains functions to perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
#the module provides addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division functions
#all the functions take two numbers as argument
#creating addition function
def addition(num1,num2):
return num1+num2
#creating subtraction function
def subtraction(num1,num2):
return num1-num2
#creating multiplication function
def multiplication(num1,num2):
return num1*num2
#creating division function
def division(num1,num2):
return num1/num2
Now, we can call this module anywhere using the import command, and we can use these functions to perform the related tasks. There is no need to write the code again and again for performing addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division operations.
Call your module
Let’s call this module in our other Python script by using the import command. Check out this article (https://linuxhint.com/python_import_command/) to learn more about the Python import command.
#calling addition function from MathOperation module
#the function is called by using the module name
print("The sum is:",MathOperation.addition(10,4))
#calling subtraction function
print("The difference is: ",MathOperation.subtraction(100,34))
#calling multiplication function
print("The multiplication is: ",MathOperation.multiplication(4,3))
#calling division function
print("The division result is:",MathOperation.division(200,5))
Output
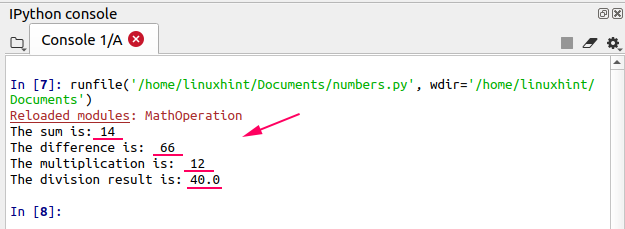
Calling the module variables
We can also declare the variables in our self-created Python modules, assign values to those variables, and call them in our Python script. The modules can also contain dictionaries, lists, etc.
num1 = 10
num2 = 20
#creating the student list
student = ['John','Mark','Taylor','David']
#creating the student dictionary
std_dict = {'name':'Ali','age':12,'email':'ali@xyz.com'}
Now let’s call the variables and objects in other Python script.
#import the module
import MathOperation
#calling the variable num1
print("The num1 value is:",MathOperation.num1)
#calling the variable num2
print("The num1 value is:",MathOperation.num2)
#calling the student list
print("The num1 value is:",MathOperation.student)
#calling the student's list items
print(MathOperation.student[0])
print(MathOperation.student[1])
print(MathOperation.student[2])
print(MathOperation.student[3])
#printing the student dictionary
print(MathOperation.std_dict)
#calling the student's dictionary items
print(MathOperation.std_dict['name'])
print(MathOperation.std_dict['age'])
print(MathOperation.std_dict['email'])
Output
The output shows that we have successfully accessed the variables and functions from the “MathOperation” module.
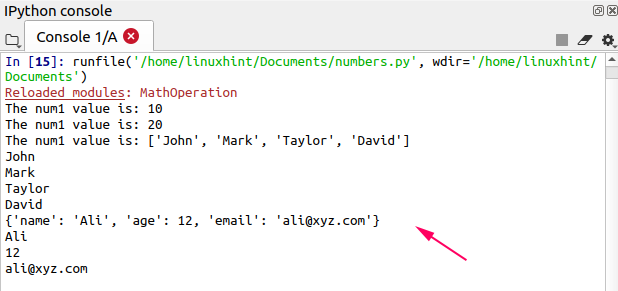
List all the functions and variables of a module
Python provides a built-in dir() function, which lists down the names of all functions and variables that are present in a particular module. Let’s use the dir() function to list down the names of functions and variables of the “MathOperation” module.
These our functions and variables that are created in our “MathOperation” module.
#the module provides addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division functions
#all the functions take two numbers as argument
#creating addition function
def addition(num1,num2):
return num1+num2
#creating subtraction function
def subtraction(num1,num2):
return num1-num2
#creating multiplication function
def multiplication(num1,num2):
return num1*num2
#creating division function
def division(num1,num2):
return num1/num2
#creating variables
num1 = 10
num2 = 20
#creating the student list
student = ['John','Mark','Taylor','David']
#creating the student dictionary
std_dict = {'name':'Ali','age':12,'email':'ali@xyz.com'}
Now let’s call the dir() function in our Python script.
import MathOperation
#using the dir() function
print(dir(MathOperation))
Output
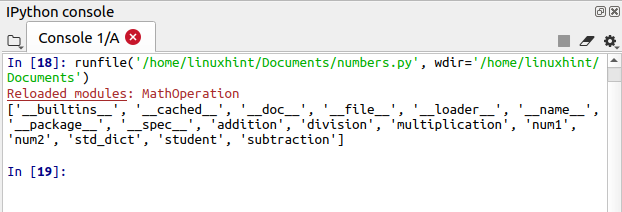
Conclusion
Although Python provides many built-in modules and functions to perform some specific task, we can also create our own Python modules. A Python module contains functions and variables. The Python modules are saved with the .py extension. This article explains the creation of your own Python modules with the help of simple examples.
from Linux Hint https://ift.tt/35THVLW




0 Comments