Usage of Built-in Facades
You must create a controller to use any built-in facade. Run the following command to create a controller named TestController.

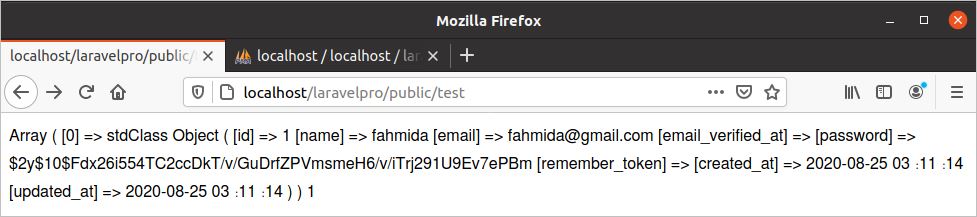
Modify the TestController with the following code to show the use of the built-in facade DB. This facade is used to do all types of database operations. In the following code, all records of the user’s table will be retrieved by using the DB façade. The output will be printed as an array after executing the code.
TestController.php:
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use DB;
class TestController extends Controller
{
public function index()
{
$users = DB::select('select * from users');
echo print_r($users);
}
}
Add the following route in the web.php file. This will call the index() method TestController for the route ‘/test.’
Run the following URL from the browser.
http://localhost/laravelpro/public/test
Create a Facade
Follow the steps below to create a custom facade in Laravel.
1. Create a folder named Area under the app folder and create a file named Area.php under this folder with the following code. Four methods are defined in the class to calculate the area of a circle, square, rectangle, and triangle. Circle() will take the radius value as a parameter to calculate the area. Square() will take the length of each side of the square as a parameter to calculate the area. Rectangle() will take the height and width as parameters to calculate the area. Triangle() will take the base and height values of the triangle to calculate the area.
namespace App\Area;
class Area
{
public function Circle($radius)
{
return "The area of the circle is ".(3.14*$radius*$radius);
}
public function Square($len)
{
return "The area of sqaure is ".($len*$len);
}
public function Rectangle($height,$width)
{
return "The area of rectangle is ".($height*$width);
}
public function Triangle($base,$height)
{
return "The area of triangle is ".(0.5*$base*$height);
}
}
2. Add the following routes to access the methods of the Area class. Here, when the user types ‘area’ after the base URL, an object of the Area class will be defined, and the four methods of this class are called with parameter values. But, if you want to access the methods of the class directly like a facade without creating the object, then an error will be generated. The next steps show you how to create a facade to access the methods of this class directly.
Route::get('/area', function () {
$area = new Area();
echo $area->Circle(3)."<br/>";
echo $area->Square(4)."<br/>";
echo $area->Rectangle(100,200)."<br/>";
echo $area->Triangle(10,5)."<br/>";
});
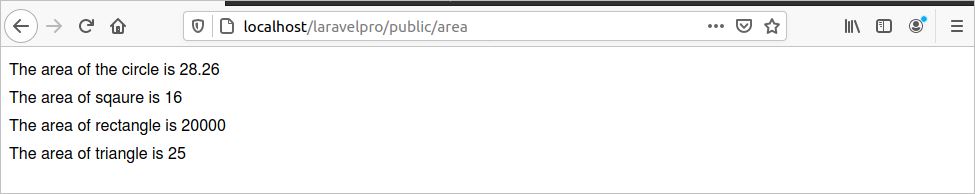
3. Run the following URL from the browser to check whether the route is working.
http://localhost/laravelpro/public/area
The following output will appear if the route works properly.
4. Create a folder named Facades under the app folder and create a file named CalculateArea.php with the following code. Here, the getFacadeAccessor() method is defined inside CalculateArea to return the string cal_area used to bind the Area class.
namespace App\Facades;
class CalculateArea extends \Illuminate\Support\Facades\Facade
{
public static function getFacadeAccessor()
{
return 'cal_area';
}
}
5. Open web.php and add the following code to bind the Area class with CalculateArea facade class by the string cal_area.
return new \App\Area\Area;
});
6. Open the app.php file under the config folder. Go to the aliases array section and add the following line at the end of the array. This defines CalculateArea as an array index and the value is the facade class that is defined under the /app/facade folder. Now, you can access the methods of the Area class as a facade without creating any object.
7. Add the following route in the web.php file to access the methods of the Area class using the CalculateArea facade.
echo CalculateArea::Circle(3)."<br/>";
echo CalculateArea::Square(4)."<br/>";
echo CalculateArea::Rectangle(100,200)."<br/>";
echo CalculateArea::Triangle(10,5)."<br/>";
});
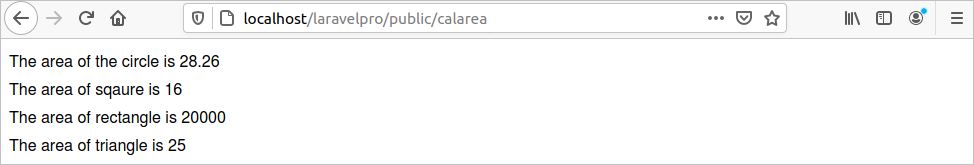
8. Run the following URL from the browser to check whether the route is working.
http://localhost/laravelpro/public/calarea
The following output will appear if the route works properly.
9. You can also use the CalculateArea facade like a built-in facade in any controller. Run the following command to create a controller named FacadeController where the CalculateArea facade will be applied.
Modify the controller with the following code, where the CalculateArea facade is imported and the index() method is added inside the controller. When the index() method is called, the four methods of the Area class will be called, and the formatted outputs will be printed by using CSS.
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use CalculateArea;
class FacadeController extends Controller
{
public function index()
{
echo "<p style='color:blue'>".CalculateArea::Circle(5)."</p>";
echo "<p style='color:red'>".CalculateArea::Square(5)."</p>";
echo "<p style='color:green'>".CalculateArea::Rectangle(200,200)."</p>";
echo "<p style='color:yellow'>".CalculateArea::Triangle(15,5)."</p>";
}
}
10. Add the following route in web.php to access to access the index() method of FacadeController.
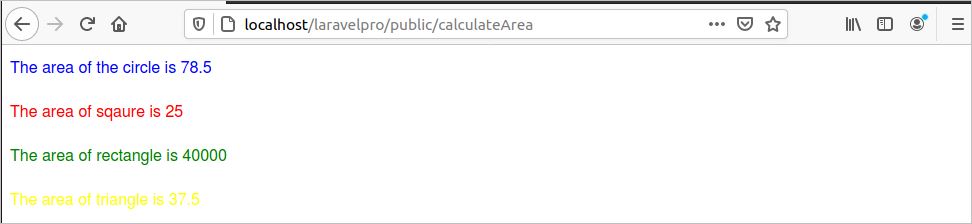
11. Run the following URL from the browser to check whether the route is working.
http://localhost/laravelpro/public/calculateArea
The following output will appear if the route works properly.
Conclusion
The feature discussed in this article can be used in different places, like the controller or route of Laravel, by using facade. This makes the development task easier. The uses of both built-in and user-defined facades are explained in this tutorial by using appropriate examples. The use of a built-in facade, DB, is shown by using a controller. The use of a custom facade, CalculateArea, is shown by using a route and a controller. This tutorial explained the concept of using a facade to help Laravel developers to apply it in their projects, based on their specific requirements.
from Linux Hint https://ift.tt/32Rwzbi




0 Comments