It is always recommended to have private docker registry or repository in your Kubernetes cluster. Docker private registry allows the developers to push and pull their private container images. Once the application’s containers are pushed to private registry then developers can use the path of their private registry while creating and deploying their yaml files.
In this article, we will learn how we can deploy private docker registry as a deployment on top of Kubernetes cluster. I am assuming Kubernetes cluster is already up and running.
Kubernetes lab details for setting up private docker registry
- k8s-master – 192.168.1.40 – CentOS 7
- k8s-worker-1 – 192.168.1.41 – CentOS 7
- k8s-worker-2 – 192.168.1.42 – CentOS 7
- kadmin user with sudo rights
- NFS share ‘/opt/certs’ & ‘/opt/registry’
Note: In my case, I have setup nfs server on master node and exported /opt/certs and /opt/registry as nfs share.
Before starting the deployment of private registry, please make sure these nfs shares are mounted on each worker nodes. Run the following commands on each worker node.
$ sudo mkdir /opt/certs /opt/registry $ sudo mount 192.168.1.40:/opt/certs /opt/certs $ sudo mount 192.168.1.40:/opt/registry /opt/registry
For permanent mount, add nfs entries in /etc/fstab file.
In place of mounting these nfs shares, we can also create nfs based persistent volumes and later we can use these persistent volumes in yaml file.
Let’s dive into installation and configuration steps of private docker registry in Kubernetes.
Step 1) Generate self-signed certificates for private registry
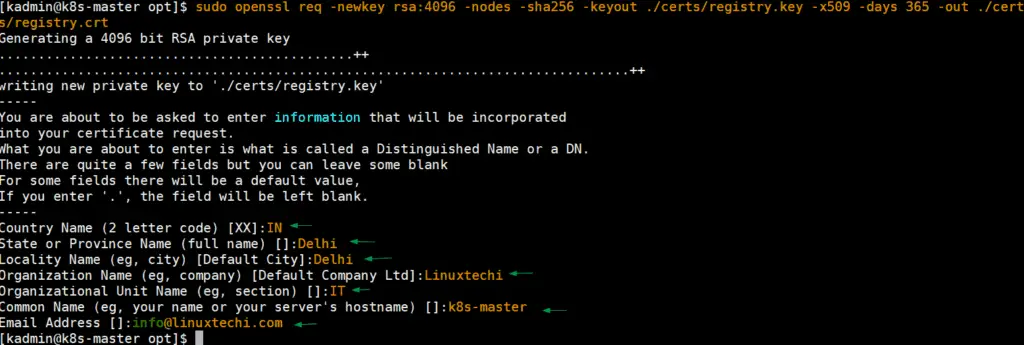
Login to your control plane or master node and use openssl command to generate self-signed certificates for private docker repository.
[kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ cd /opt [kadmin@k8s-master opt]$ sudo openssl req -newkey rsa:4096 -nodes -sha256 -keyout ./certs/registry.key -x509 -days 365 -out ./certs/registry.crt
Once the key and certificate file are generated, use ls command to verify them,
[kadmin@k8s-master opt]$ ls -l certs/ total 8 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2114 Sep 26 03:26 registry.crt -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 3272 Sep 26 03:26 registry.key [kadmin@k8s-master opt]$
Step 2) Deploy private registry as deployment via yaml file
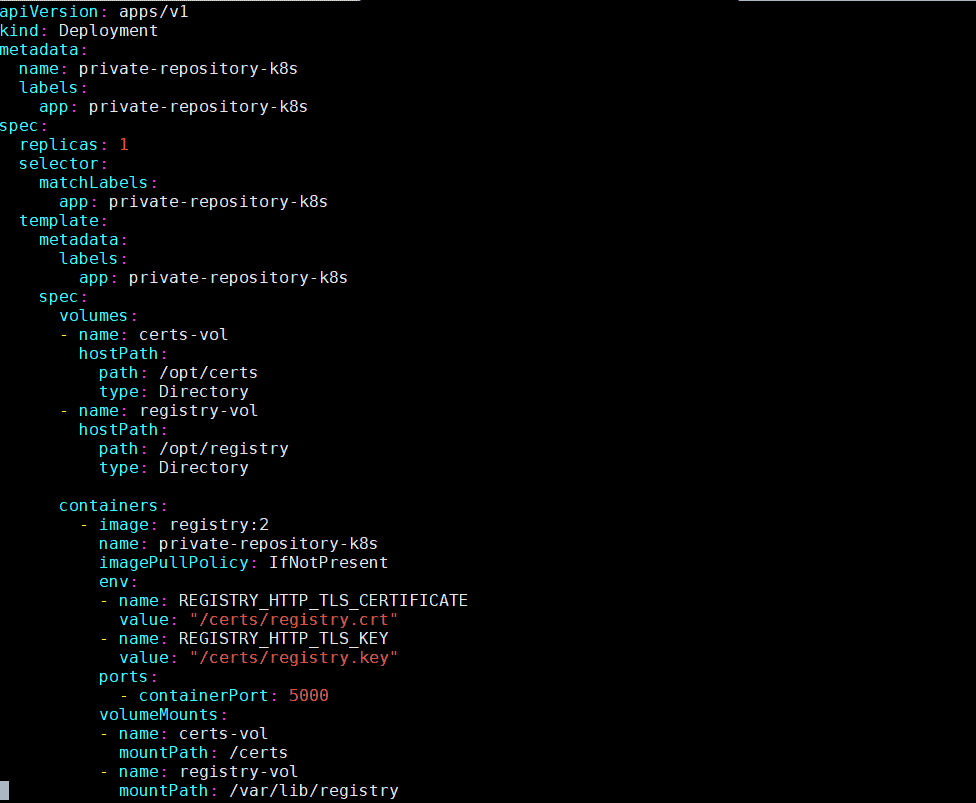
On your master node, create a private-registry.yaml file with the following contents
[kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ mkdir docker-repo
[kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ cd docker-repo/
[kadmin@k8s-master docker-repo]$ vi private-registry.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: private-repository-k8s
labels:
app: private-repository-k8s
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: private-repository-k8s
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: private-repository-k8s
spec:
volumes:
- name: certs-vol
hostPath:
path: /opt/certs
type: Directory
- name: registry-vol
hostPath:
path: /opt/registry
type: Directory
containers:
- image: registry:2
name: private-repository-k8s
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
env:
- name: REGISTRY_HTTP_TLS_CERTIFICATE
value: "/certs/registry.crt"
- name: REGISTRY_HTTP_TLS_KEY
value: "/certs/registry.key"
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
volumeMounts:
- name: certs-vol
mountPath: /certs
- name: registry-vol
mountPath: /var/lib/registry
save and close the yaml file
Run the following kubectl command deploy the private registry using above created yaml file,
[kadmin@k8s-master docker-repo]$ kubectl create -f private-registry.yaml deployment.apps/private-repository-k8s created [kadmin@k8s-master docker-repo]$
Execute below kubectl commands to verify status of registry deployment and its pod.
[kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ kubectl get deployments private-repository-k8s NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE private-repository-k8s 1/1 1 1 3m32s [kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ [kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ kubectl get pods | grep -i private-repo private-repository-k8s-85cf76b9d7-qsjxq 1/1 Running 0 5m14s [kadmin@k8s-master ~]$
Perfect, above output confirms that registry has been deployed successfully, Now copy the registry certificate file to worker nodes and master node under the folder “/etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors“. Execute the following commands on master node and each worker nodes
$ sudo cp /opt/certs/registry.crt /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/ $ sudo update-ca-trust $ sudo systemctl restart docker
Step 3) Expose registry deployment as a nodeport service type
To expose registry deployment as a nodeport service type, create the following yaml file with the beneath contents,
[kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ cd docker-repo/
[kadmin@k8s-master docker-repo]$ vi private-registry-svc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: private-repository-k8s
name: private-repository-k8s
spec:
ports:
- port: 5000
nodePort: 31320
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 5000
selector:
app: private-repository-k8s
type: NodePort
save and close the file.
Now deploy the service by running following kubectl command,
[kadmin@k8s-master docker-repo]$ kubectl create -f private-registry-svc.yaml service/private-repository-k8s created [kadmin@k8s-master docker-repo]$
Run below kubectl command to verify the service status,
[kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ kubectl get svc private-repository-k8s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
private-repository-k8s NodePort 10.100.113.39 <none> 5000:31320/TCP 2m1s
[kadmin@k8s-master ~]$
Step 4) Test and Use private docker registry in k8s
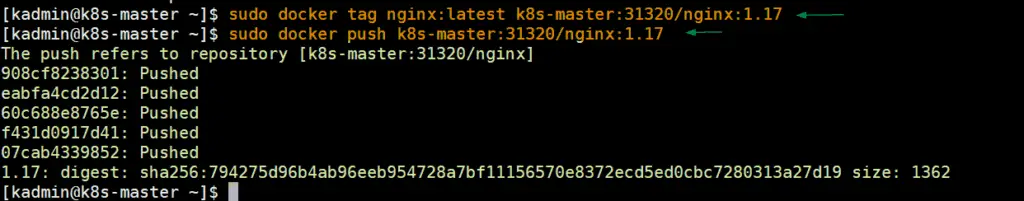
To test private registry, we will download nginx image locally and then will upload that image to private registry, from the master node run the following set of commands,
[kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ sudo docker pull nginx [kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ sudo docker tag nginx:latest k8s-master:31320/nginx:1.17 [kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ sudo docker push k8s-master:31320/nginx:1.17
Output of above command would like below:
Run below docker command to verify whether nginx is uploaded to private repository or not.
[kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ sudo docker image ls | grep -i nginx
nginx latest 7e4d58f0e5f3 2 weeks ago 133MB
k8s-master:31320/nginx 1.17 7e4d58f0e5f3 2 weeks ago 133MB
[kadmin@k8s-master ~]$
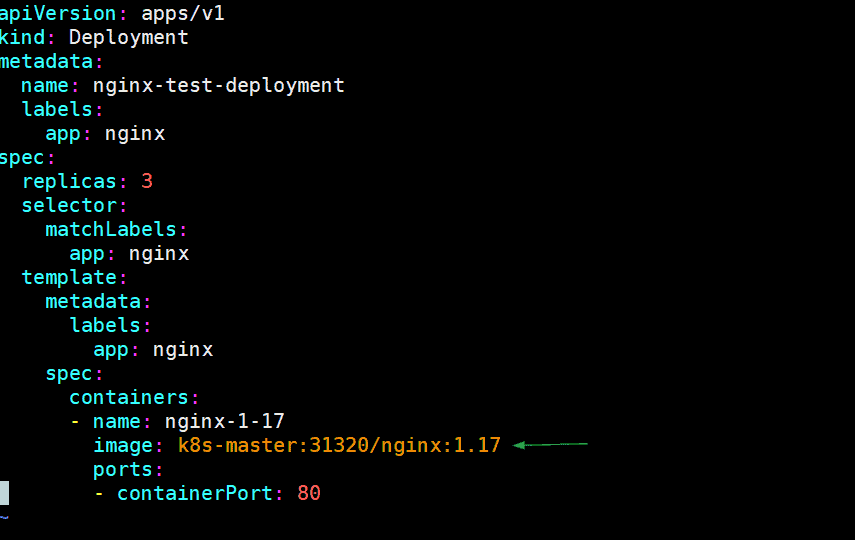
Now, let’s deploy a nginx based deployment and in the yaml file specify the image’s path as our private docker registry. Example is shown below:
[kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ vi nginx-test-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-test-deployment
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-1-17
image: k8s-master:31320/nginx:1.17
ports:
- containerPort: 80
Save and Close the file
Run following kubectl commands,
[kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ kubectl create -f nginx-test-deployment.yaml deployment.apps/nginx-test-deployment created [kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ kubectl get deployments nginx-test-deployment NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE nginx-test-deployment 3/3 3 3 13s [kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ [kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ kubectl get pods | grep nginx-test-deployment nginx-test-deployment-f488694b5-2rvmv 1/1 Running 0 80s nginx-test-deployment-f488694b5-8kb6c 1/1 Running 0 80s nginx-test-deployment-f488694b5-dgcxl 1/1 Running 0 80s [kadmin@k8s-master ~]$
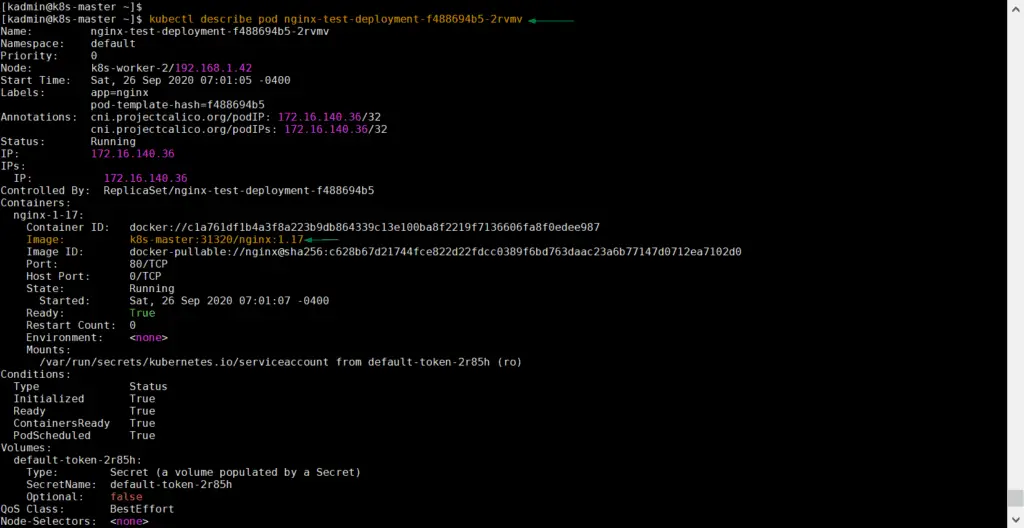
Try to describe any pod using ‘kubectl describe‘ command and verify image path
[kadmin@k8s-master ~]$ kubectl describe pod nginx-test-deployment-f488694b5-2rvmv
Output of above command would be,
Above output confirms that container’s image path is our private docker registry, so it means nginx image has been downloaded from private registry. That’s all from this article, I hope these steps help you to setup private docker registry on your Kubernetes cluster. Please do share your feedback and comments in the comments section below.
The post How to Setup Private Docker Registry in Kubernetes (k8s) first appeared on Linuxtechi.
from Linuxtechi https://ift.tt/2G9uGxz




0 Comments