Syntax
- One-dimensional Array
Any particular datatype must be mentioned at the time of array declaration, and the array will store the data based on that datatype.
- Two-dimensional Array
Like a one-dimensional array, a two-dimensional array requires mentioning the datatype, and two pairs of third brackets are needed to define the declaration. This type of array will store data in a tabular format that contains a fixed number of rows and columns.
Example 1: Declare, Initialize, and Access One-dimensional Array
The following example shows the uses of different one-dimensional arrays in Java. First, a numeric array object of two elements is declared and initialized with two integer values. Next, a character array object of three elements is declared and two characters are assigned in the first and third index. Then, a string array of four elements is declared and three values are serially assigned in the three indexes. The values of the integer and character arrays are printed by mentioning the index, and the values of the string arrays are printed using the ‘for’ loop.
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Declare a numeric array
int num_arr[] = new int[2];
//Assign values
num_arr[0] = 50;
num_arr[1] = 100;
//Declare a character array
char char_arr[] = new char[3];
//Assign values
char_arr[0] = 'A';
char_arr[2] = 'C';
//Declare a String array
String[] str_arr = new String[4];
//Assign values
str_arr[0] = "Mango";
str_arr[1] = "Banana";
str_arr[2] = "Orange";
System.out.print("\nThe values of numeric array are : "+num_arr[0]+" "+num_arr[1]+"\n");
System.out.print("The values of character array are : "+char_arr[0]+" "+char_arr[2]+"\n");
System.out.print("The values of string array are : ");
//Iterate the array using loop
for (int i = 0; i < str_arr.length; i++)
System.out.print(str_arr[i]+" ");
}
}
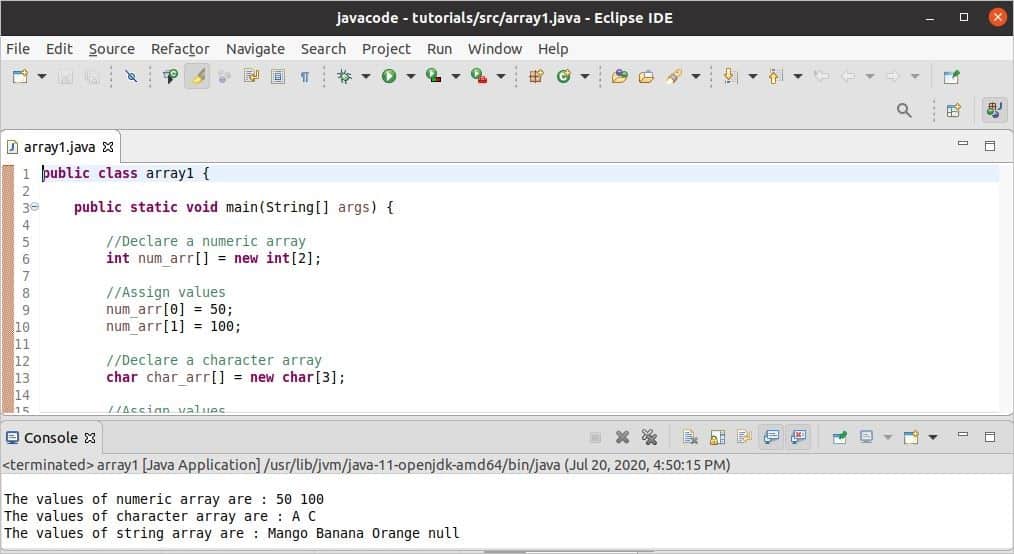
Output:
The following image shows the output of the code. Here, the values of the first two arrays are printed based on the index value assigned. The last index of the third array is not assigned, and the null value is assigned by default on the last index for the printed string array.
Example 2: Declare an Array with Values and Sort the Array
The array values are initialized separately by the index in the previous example. This example shows how the array values can be initialized at the time of array declaration. Here, a numeric array of eight elements with values is declared in the code. Next, the values are printed using the ‘for’ loop. Java array has a built-in sort() method to sort array values. The array values are sorted using this method and printed using the ‘for’ loop again.
public class array2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Initialize a numeric array
int num_arr[] = {67, 89, 20, 61, 75, 49, 36, 15};
System.out.print("Array before sort\n");
//Iterate the array using loop
for (int i = 0; i < num_arr.length; i++)
System.out.print(num_arr[i]+" ");
//Sort the array using sort() method
Arrays.sort(num_arr);
System.out.print("\n\nArray after sort\n");
for (int i = 0; i < num_arr.length; i++)
System.out.print(num_arr[i]+" ");
}
}
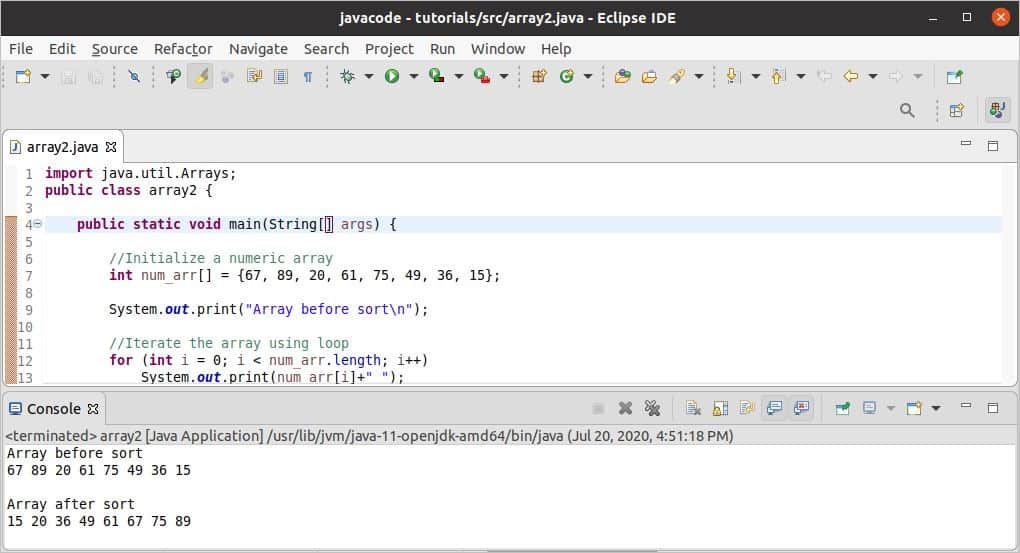
Output:
The following image shows the output of the code. First, all values of the array are printed, and the next sorted array values are printed in ascending order.
Example 3: Declare, Initialize and Access Two-dimensional Array
This example illustrates how a two-dimensional array can be declared, initialized, and accessed using Java. You must use two ‘[]’ brackets to define the two dimensions of the array. The row numbers are defined in the first pair of the third bracket, and the column numbers are defined in the second pair of the third brackets. The code shows two ways of declaring a two-dimensional array. At first, a two-dimensional array named score is declared that contains two rows and two columns. Four numeric values are later assigned in the four indexes, and two values are printed. Next, a two-dimensional array of four rows and three columns, named customers, is declared with values. A ‘for’ loop is used to read each value of the array. The loop will iterate four times to read four rows of the array and will read the values of each column, printing the formatted output in each iteration.
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Declare a two-dimensional numeric array with length
int[][] score=new int[2][2];
//Initialize the array with values
score[0][0] = 1001;
score[0][1] = 700;
score[1][0] = 1002;
score[1][1] = 900;
//Print the array values
System.out.print("The score of " + score[1][0] + " is " + score[1][1]);
//Declare a two-dimensional string array with values
String customer[][]={{"67453","Meher Afroze","CEO"},
{"26368","Ali Mahmud","Manager"},
{"72443","Abrar Zahin","GM"},
{"20332","Hasan Mahmud","MD"}};
//Iterate the array values using for loop
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
System.out.print("\nThe post of " + customer[i][1]+"("+customer[i][0]+")" +
" is " + customer[i][2]);
}
}
}
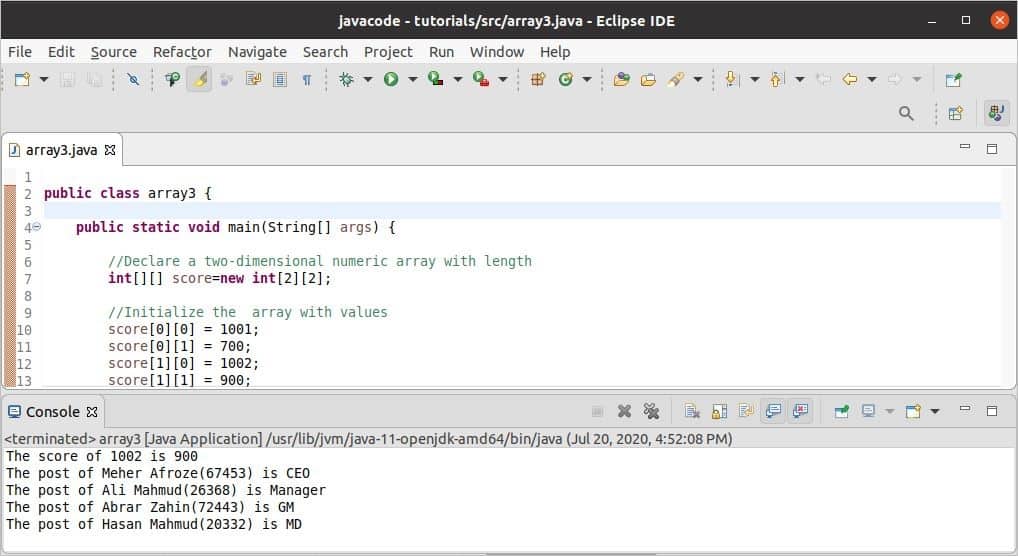
Output:
The following image shows the output of the code. The first line shows the output of the score array, and the last four lines show the output of the customer array.
Conclusion
The basic uses of one-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays in Java are explained in this tutorial through some very simple examples. This tutorial will help new Java users learn the concept of using arrays and how to properly apply this method in their code.
from Linux Hint https://ift.tt/33ioyfY




0 Comments