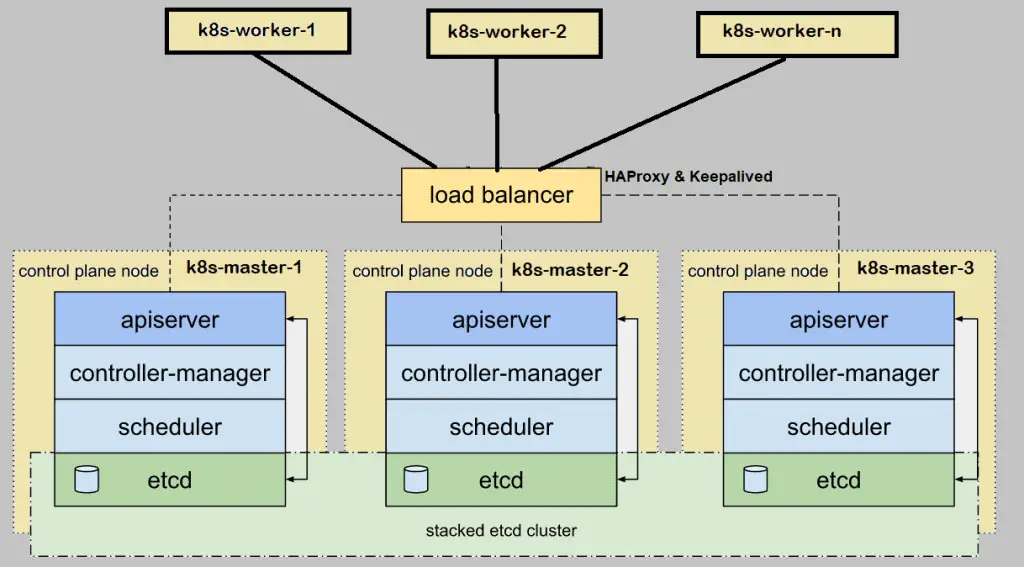
When we setup Kubernetes (k8s) cluster on-premises for production environment then it is recommended to deploy it in high availability. Here high availability means installing Kubernetes master or control plane in HA. In this article I will demonstrate how we can setup highly available Kubernetes cluster using kubeadm utility.
For the demonstration, I have used five CentOS 7 systems with following details:
- k8s-master-1 – Minimal CentOS 7 – 192.168.1.40 – 2GB RAM, 2vCPU, 40 GB Disk
- k8s-master-2 – Minimal CentOS 7 – 192.168.1.41 – 2GB RAM, 2vCPU, 40 GB Disk
- k8s-master-3 – Minimal CentOS 7 – 192.168.1.42 – 2GB RAM, 2vCPU, 40 GB Disk
- k8s-worker-1 – Minimal CentOS 7 – 192.168.1.43 – 2GB RAM, 2vCPU, 40 GB Disk
- k8s-worker-2 – Minimal CentOS 7 – 192.168.1.44 – 2GB RAM, 2vCPU, 40 GB Disk
Note: etcd cluster can also be formed outside of master nodes but for that we need additional hardware, so I am installing etcd inside my master nodes.
Minimum requirements for setting up Highly K8s cluster
- Install Kubeadm, kubelet and kubectl on all master and worker Nodes
- Network Connectivity among master and worker nodes
- Internet Connectivity on all the nodes
- Root credentials or sudo privileges user on all nodes
Let’s jump into the installation and configuration steps
Step 1) Set Hostname and add entries in /etc/hosts file
Run hostnamectl command to set hostname on each node, example is shown for k8s-master-1 node,
$ hostnamectl set-hostname "k8s-master-1" $ exec bash
Similarly, run above command on remaining nodes and set their respective hostname. Once hostname is set on all master and worker nodes then add the following entries in /etc/hosts file on all the nodes.
192.168.1.40 k8s-master-1 192.168.1.41 k8s-master-2 192.168.1.42 k8s-master-3 192.168.1.43 k8s-worker-1 192.168.1.44 k8s-worker-2 192.168.1.45 vip-k8s-master
I have used one additional entry “192.168.1.45 vip-k8s-master” in host file because I will be using this IP and hostname while configuring the haproxy and keepalived on all master nodes. This IP will be used as kube-apiserver load balancer ip. All the kube-apiserver request will come to this IP and then the request will be distributed among backend actual kube-apiservers.
Step 2) Install and Configure Keepalive and HAProxy on all master / control plane nodes
Install keepalived and haproxy on each master node using the following yum command,
$ sudo yum install haproxy keepalived -y
Configure Keepalived on k8s-master-1 first, create check_apiserver.sh script will the following content,
[kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$ sudo vi /etc/keepalived/check_apiserver.sh
#!/bin/sh
APISERVER_VIP=192.168.1.45
APISERVER_DEST_PORT=6443
errorExit() {
echo "*** $*" 1>&2
exit 1
}
curl --silent --max-time 2 --insecure https://localhost:${APISERVER_DEST_PORT}/ -o /dev/null || errorExit "Error GET https://localhost:${APISERVER_DEST_PORT}/"
if ip addr | grep -q ${APISERVER_VIP}; then
curl --silent --max-time 2 --insecure https://${APISERVER_VIP}:${APISERVER_DEST_PORT}/ -o /dev/null || errorExit "Error GET https://${APISERVER_VIP}:${APISERVER_DEST_PORT}/"
fi
save and exit the file.
Set the executable permissions
$ sudo chmod +x /etc/keepalived/check_apiserver.sh
Take the backup of keepalived.conf file and then truncate the file.
[kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$ sudo cp /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf-org [kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$ sudo sh -c '> /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf'
Now paste the following contents to /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf file
[kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$ sudo vi /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
! /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
router_id LVS_DEVEL
}
vrrp_script check_apiserver {
script "/etc/keepalived/check_apiserver.sh"
interval 3
weight -2
fall 10
rise 2
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state MASTER
interface enp0s3
virtual_router_id 151
priority 255
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass P@##D321!
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.1.45/24
}
track_script {
check_apiserver
}
}
Save and close the file.
Note: Only two parameters of this file need to be changed for master-2 & 3 nodes. State will become SLAVE for master 2 and 3, priority will be 254 and 253 respectively.
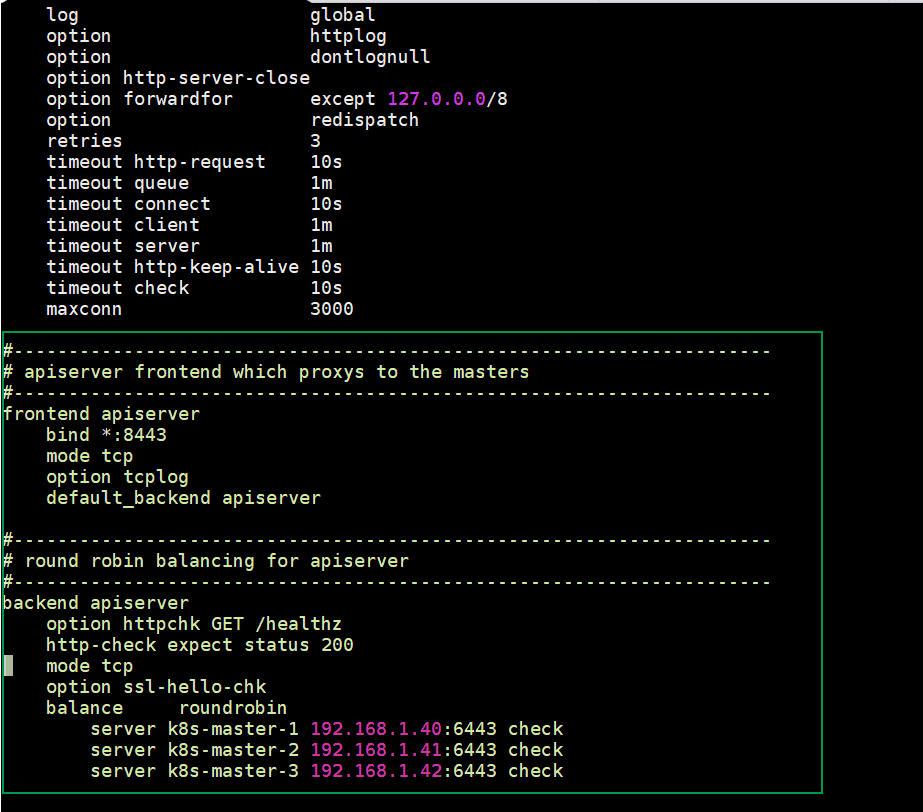
Configure HAProxy on k8s-master-1 node, edit its configuration file and add the following contents:
[kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$ sudo cp /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg-org
Remove all lines after default section and add following lines
[kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$ sudo vi /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# apiserver frontend which proxys to the masters
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
frontend apiserver
bind *:8443
mode tcp
option tcplog
default_backend apiserver
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# round robin balancing for apiserver
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
backend apiserver
option httpchk GET /healthz
http-check expect status 200
mode tcp
option ssl-hello-chk
balance roundrobin
server k8s-master-1 192.168.1.40:6443 check
server k8s-master-2 192.168.1.41:6443 check
server k8s-master-3 192.168.1.42:6443 check
Save and exit the file
Now copy theses three files (check_apiserver.sh , keepalived.conf and haproxy.cfg) from k8s-master-1 to k8s-master-2 & 3
Run the following for loop to scp these files to master 2 and 3
[kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$ for f in k8s-master-2 k8s-master-3; do scp /etc/keepalived/check_apiserver.sh /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf root@$f:/etc/keepalived; scp /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg root@$f:/etc/haproxy; done
Note: Don’t forget to change two parameters in keepalived.conf file that we discuss above for k8s-master-2 & 3
In case firewall is running on master nodes then add the following firewall rules on all three master nodes
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-rich-rule='rule protocol value="vrrp" accept' --permanent $ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=8443/tcp $ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Now Finally start and enable keepalived and haproxy service on all three master nodes using the following commands :
$ sudo systemctl enable keepalived --now $ sudo systemctl enable haproxy --now
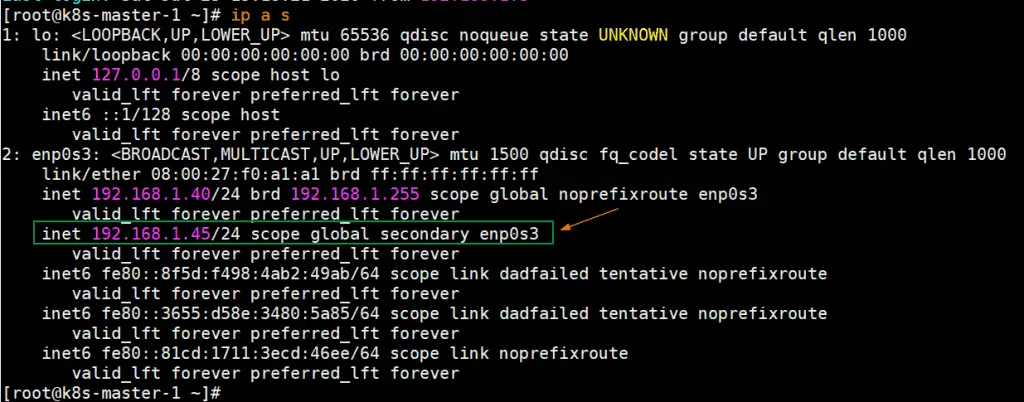
Once these services are started successfully, verify whether VIP (virtual IP) is enabled on k8s-master-1 node because we have marked k8s-master-1 as MASTER node in keepalived configuration file.
Perfect, above output confirms that VIP has been enabled on k8s-master-1.
Step 3) Disable Swap, set SELinux as permissive and firewall rules for Master and worker nodes
Disable Swap Space on all the nodes including worker nodes, Run the following commands
$ sudo swapoff -a $ sudo sed -i '/ swap / s/^\(.*\)$/#\1/g' /etc/fstab
Set SELinux as Permissive on all master and worker nodes, run the following commands,
$ sudo setenforce 0 $ sudo sed -i 's/^SELINUX=enforcing$/SELINUX=permissive/' /etc/selinux/config
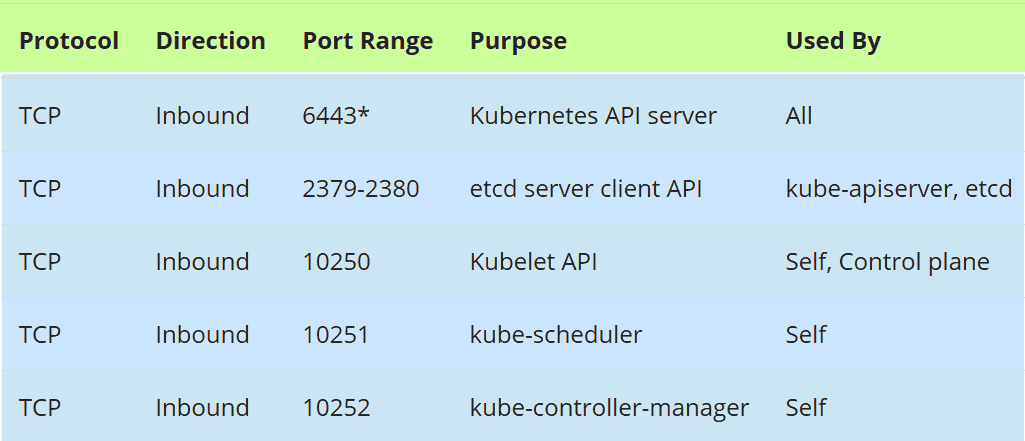
Firewall Rules for Master Nodes:
In case firewall is running on master nodes, then allow the following ports in the firewall,
Run the following firewall-cmd command on all the master nodes,
$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=6443/tcp $ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=2379-2380/tcp $ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10250/tcp $ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10251/tcp $ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10252/tcp $ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=179/tcp $ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=4789/udp $ sudo firewall-cmd --reload $ sudo modprobe br_netfilter $ sudo sh -c "echo '1' > /proc/sys/net/bridge/bridge-nf-call-iptables" $ sudo sh -c "echo '1' > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward"
Firewall Rules for Worker nodes:
In case firewall is running on worker nodes, then allow the following ports in the firewall on all the worker nodes
Run the following commands on all the worker nodes,
$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10250/tcp $ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=30000-32767/tcp $ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=179/tcp $ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=4789/udp $ sudo firewall-cmd --reload $ sudo modprobe br_netfilter $ sudo sh -c "echo '1' > /proc/sys/net/bridge/bridge-nf-call-iptables" $ sudo sh -c "echo '1' > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward"
Step 4) Install Container Run Time (CRI) Docker on Master & Worker Nodes
Install Docker (Container Run Time) on all the master nodes and worker nodes, run the following command,
$ sudo yum install -y yum-utils $ sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo $ sudo yum install docker-ce -y
Run following systemctl command to start and enable docker service, (Run this command too on all master and worker nodes)
$ sudo systemctl enable docker --now
Now, let’s install kubeadm , kubelet and kubectl in the next step
Step 5) Install Kubeadm, kubelet and kubectl
Install kubeadm, kubelet and kubectl on all master nodes as well as worker nodes. Before installing these packages first, we must configure Kubernetes repository, run the following command on each master and worker nodes,
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo [kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-\$basearch enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 repo_gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg exclude=kubelet kubeadm kubectl EOF
Now run below yum command to install these packages,
$ sudo yum install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl --disableexcludes=kubernetes
Run following systemctl command to enable kubelet service on all nodes ( master and worker nodes)
$ sudo systemctl enable kubelet --now
Step 6) Initialize the Kubernetes Cluster from first master node
Now move to first master node / control plane and issue the following command,
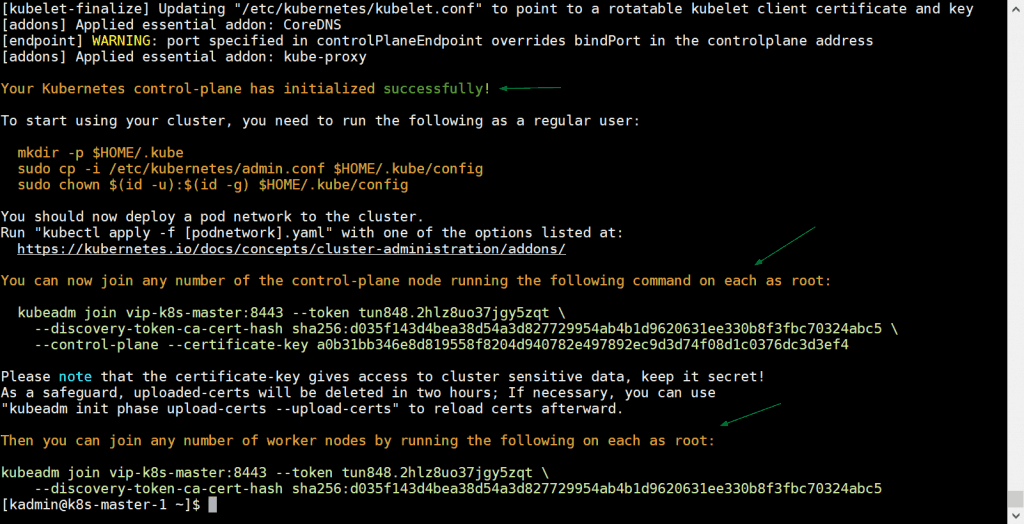
[kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$ sudo kubeadm init --control-plane-endpoint "vip-k8s-master:8443" --upload-certs
In above command, –control-plane-endpoint set dns name and port for load balancer (kube-apiserver), in my case dns name is “vip-k8s-master” and port is “8443”, apart from this ‘–upload-certs’ option will share the certificates among master nodes automatically,
Output of kubeadm command would be something like below:
Great, above output confirms that Kubernetes cluster has been initialized successfully. In output we also got the commands for other master and worker nodes to join the cluster.
Note: It is recommended to copy this output to a text file for future reference.
Run following commands to allow local user to use kubectl command to interact with cluster,
[kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$ mkdir -p $HOME/.kube [kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$ sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config [kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$ sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config [kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$
Now, Let’s deploy pod network (CNI – Container Network Interface), in my case I going to deploy calico addon as pod network, run following kubectl command
[kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$ kubectl apply -f https://docs.projectcalico.org/v3.14/manifests/calico.yaml
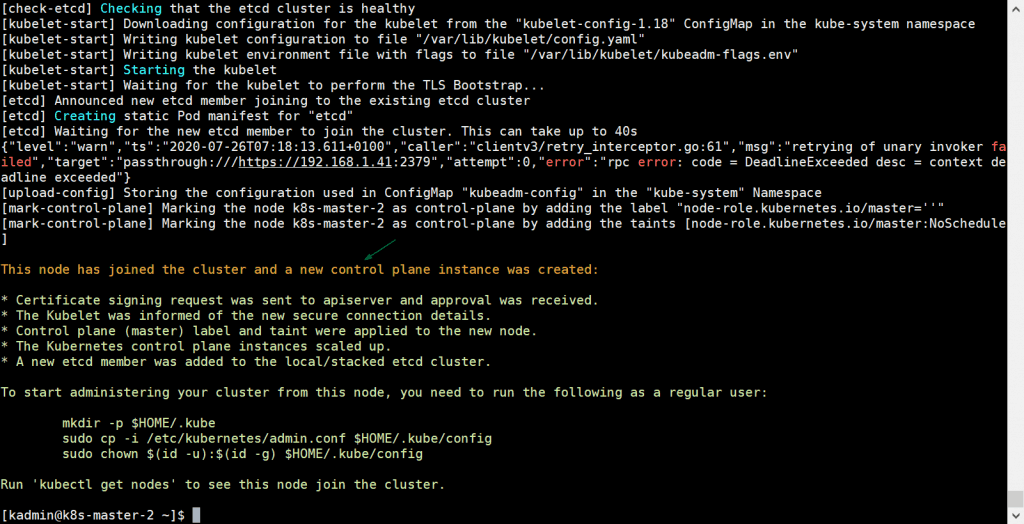
Once the pod network is deployed successfully, add remaining two master nodes to cluster. Just copy the command for master node to join the cluster from the output and paste it on k8s-master-2 and k8s-master-3, example is shown below
[kadmin@k8s-master-2 ~]$ sudo kubeadm join vip-k8s-master:8443 --token tun848.2hlz8uo37jgy5zqt --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:d035f143d4bea38d54a3d827729954ab4b1d9620631ee330b8f3fbc70324abc5 --control-plane --certificate-key a0b31bb346e8d819558f8204d940782e497892ec9d3d74f08d1c0376dc3d3ef4
Output would be:
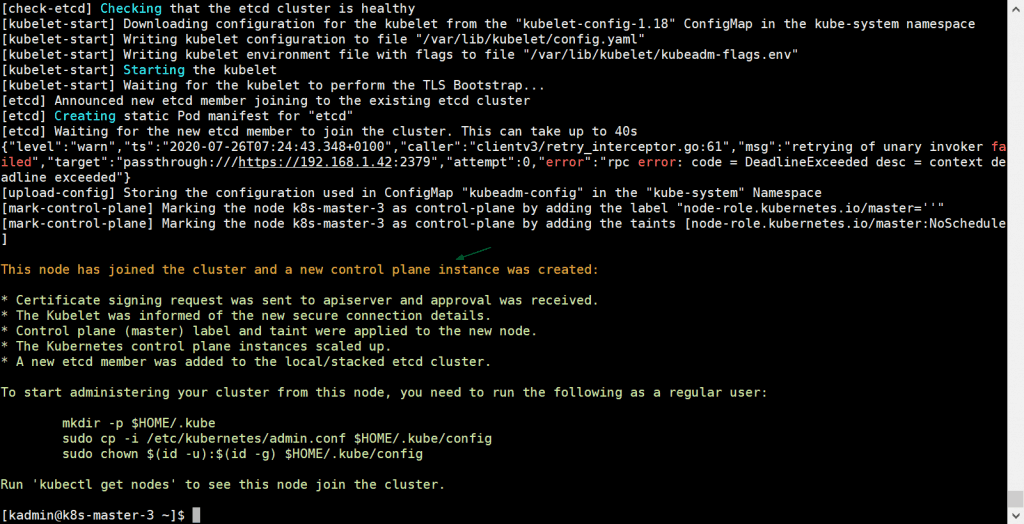
Also run the same command on k8s-master-3,
[kadmin@k8s-master-3 ~]$ sudo kubeadm join vip-k8s-master:8443 --token tun848.2hlz8uo37jgy5zqt --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:d035f143d4bea38d54a3d827729954ab4b1d9620631ee330b8f3fbc70324abc5 --control-plane --certificate-key a0b31bb346e8d819558f8204d940782e497892ec9d3d74f08d1c0376dc3d3ef4
Output would be:
Above output confirms that k8s-master-3 has also joined the cluster successfully. Let’s verify the nodes status from kubectl command, go to master-1 node and execute below command,
[kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$ kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION k8s-master-1 Ready master 31m v1.18.6 k8s-master-2 Ready master 10m v1.18.6 k8s-master-3 Ready master 3m47s v1.18.6 [kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$
Perfect, all our three master or control plane nodes are ready and join the cluster.
Step 7) Join Worker nodes to Kubernetes cluster
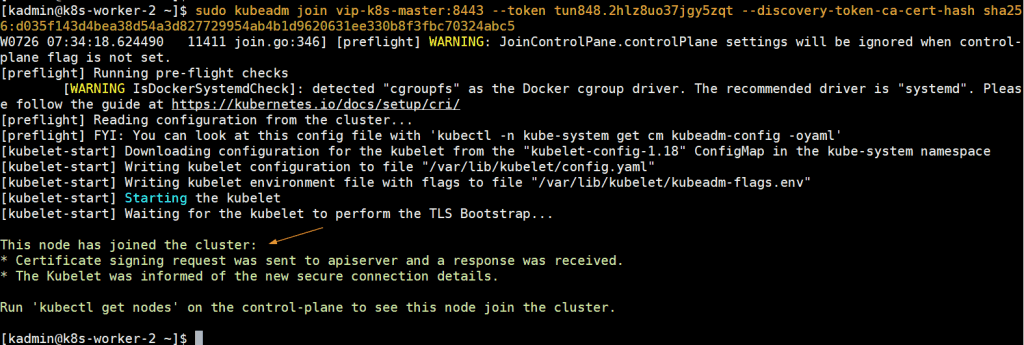
To join worker nodes to cluster, copy the command for worker node from output and past it on both worker nodes, example is shown below:
[kadmin@k8s-worker-1 ~]$ sudo kubeadm join vip-k8s-master:8443 --token tun848.2hlz8uo37jgy5zqt --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:d035f143d4bea38d54a3d827729954ab4b1d9620631ee330b8f3fbc70324abc5 [kadmin@k8s-worker-2 ~]$ sudo kubeadm join vip-k8s-master:8443 --token tun848.2hlz8uo37jgy5zqt --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:d035f143d4bea38d54a3d827729954ab4b1d9620631ee330b8f3fbc70324abc5
Output would be something like below:
Now head to k8s-master-1 node and run below kubectl command to get status worker nodes,
[kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$ kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION k8s-master-1 Ready master 43m v1.18.6 k8s-master-2 Ready master 21m v1.18.6 k8s-master-3 Ready master 15m v1.18.6 k8s-worker-1 Ready <none> 6m11s v1.18.6 k8s-worker-2 Ready <none> 5m22s v1.18.6 [kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$
Above output confirms that both workers have also joined the cluster and are in ready state.
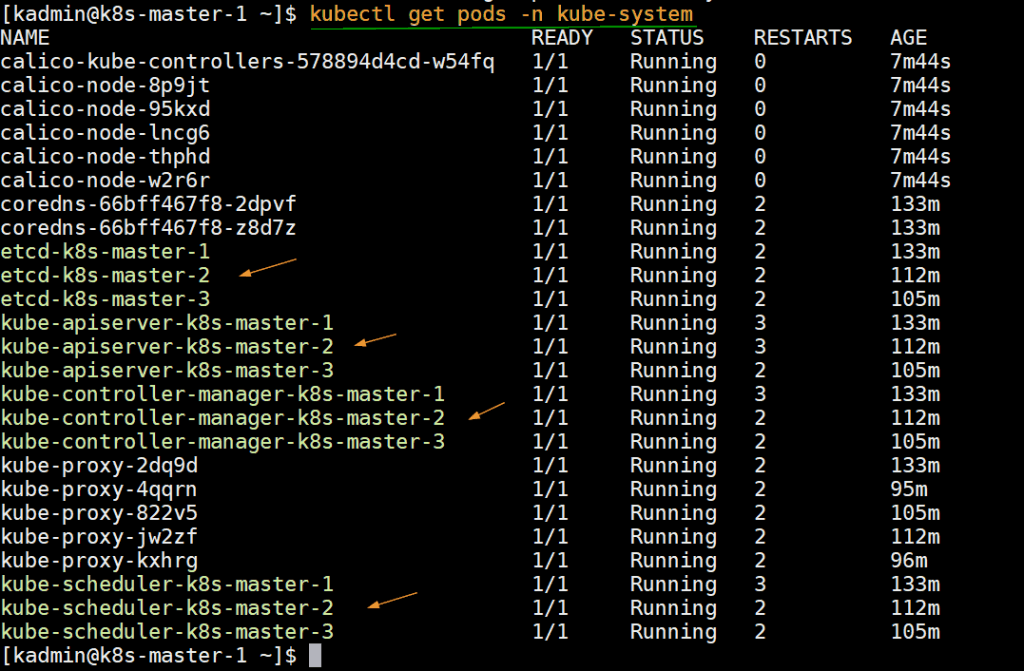
Run below command to verify the status infra pods which are deployed in kube-system namespace.
[kadmin@k8s-master-1 ~]$ kubectl get pods -n kube-system
Step 8) Test Highly available Kubernetes cluster
Let’s try to connect to the cluster from remote machine (CentOS system) using load balancer dns name and port. On the remote machine first, we must install kubectl package. Run below command to set kubernetes repositories.
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo [kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-\$basearch enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 repo_gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg exclude=kubelet kubeadm kubectl EOF $ sudo yum install -y kubectl --disableexcludes=kubernetes
Now add following entry in /etc/host file,
192.168.1.45 vip-k8s-master
Create kube directory and copy /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf file from k8s-master-1 node to $HOME/.kube/config ,
$ mkdir -p $HOME/.kube $ scp root@192.168.1.40:/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config $ sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Now run “kubectl get nodes” command,
[kadmin@localhost ~]$ kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION k8s-master-1 Ready master 3h5m v1.18.6 k8s-master-2 Ready master 163m v1.18.6 k8s-master-3 Ready master 157m v1.18.6 k8s-worker-1 Ready <none> 148m v1.18.6 k8s-worker-2 Ready <none> 147m v1.18.6 [kadmin@localhost ~]$
Let’s create a deployment with name nginx-lab with image ‘nginx’ and then expose this deployment as service of type “NodePort”
[kadmin@localhost ~]$ kubectl create deployment nginx-lab --image=nginx deployment.apps/nginx-lab created [kadmin@localhost ~]$ [kadmin@localhost ~]$ kubectl get deployments.apps nginx-lab NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE nginx-lab 1/1 1 1 59s [kadmin@localhost ~]$ kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE nginx-lab-5df4577d49-rzv9q 1/1 Running 0 68s test-844b65666c-pxpkh 1/1 Running 3 154m [kadmin@localhost ~]$
Let’s try to scale replicas from 1 to 4, run the following command,
[kadmin@localhost ~]$ kubectl scale deployment nginx-lab --replicas=4 deployment.apps/nginx-lab scaled [kadmin@localhost ~]$ [kadmin@localhost ~]$ kubectl get deployments.apps nginx-lab NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE nginx-lab 4/4 4 4 3m10s [kadmin@localhost ~]$
Now expose the deployment as service, run
[kadmin@localhost ~]$ kubectl expose deployment nginx-lab --name=nginx-lab --type=NodePort --port=80 --target-port=80
service/nginx-lab exposed
[kadmin@localhost ~]$
Get port details and try to access nginx web server using curl,
[kadmin@localhost ~]$ kubectl get svc nginx-lab
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx-lab NodePort 10.102.32.29 <none> 80:31766/TCP 60s
[kadmin@localhost ~]$
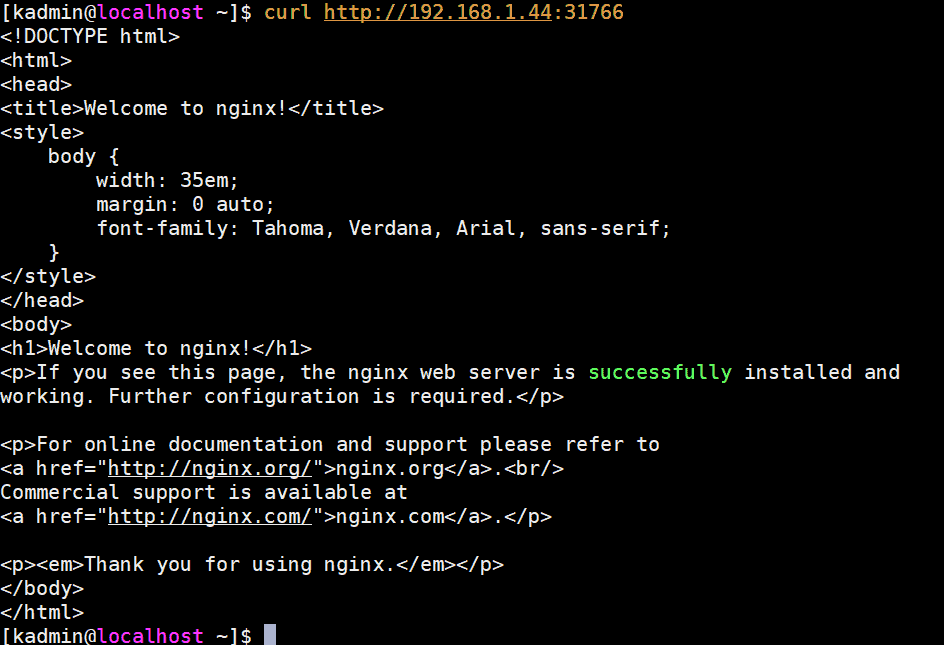
To access nginx web server we can use any master or worker node IP and port as “31766”
[kadmin@localhost ~]$ curl http://192.168.1.44:31766
Output would be something like below:
Perfect, that’s confirm we have successfully deployed highly available Kubernetes cluster with kubeadm on CentOS 7 servers. Please don’t hesitate to share your valuable feedback and comments.
Also Read : How to Setup NGINX Ingress Controller in Kubernetes
from Linuxtechi https://ift.tt/2CNRfGY




0 Comments