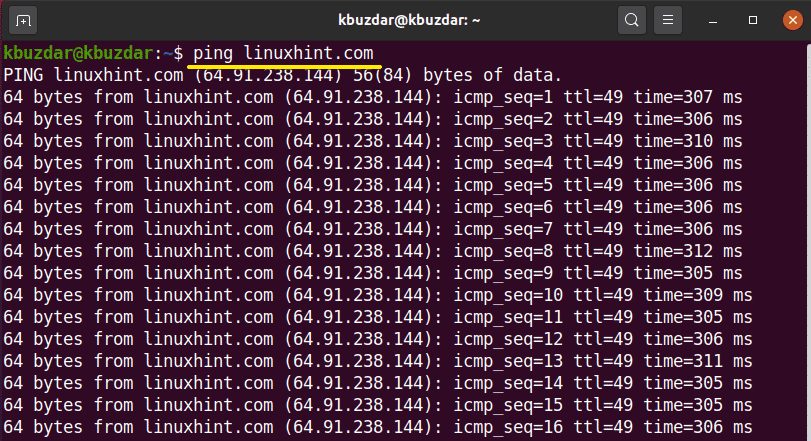
Ping is also used to assess the total time it takes to packet send and receives an acknowledgment from the connected network. In this article, you will learn the basic uses of ping command in the Linux system. We have executed all the below mentioned commands on Ubuntu 20.04.
Syntax of the ping command
The basic syntax of the ping command is as follows:
In the above syntax, the hostname is the name of the website or you can use the IP address.
To check your desired host-name is working or not in this case you need to type the following command in the terminal:
Use Ctrl + C from your keyboard to terminate the process.
Use of ping command with examples in Linux
The following uses of the ping command are given below:
Check local network using the ping command
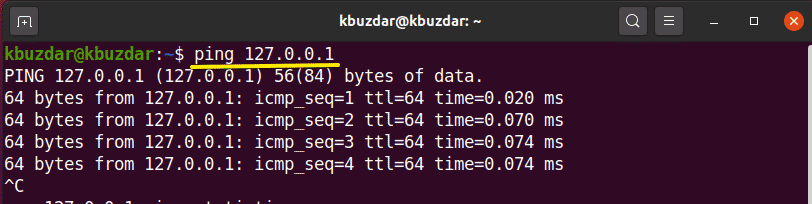
Sometimes, you encounter problems in reaching the desired website. So, in this situation, you can ping your localhost or computer system to check the proper internet connection. The following commands are useful to check your local internet connection:
Or
In the following output, you have pinged your local machine using two different ways. In the first, you use the localhost that means ‘ping to my computer’.
In the below output, using IP address ping the local computer system.
Using ping specify internet protocol
The ping command is also used to send request IPv4 or IPv6 as follows:
or
Change ping packets time interval
The default time interval between the requesting packet is 1 second in the Linux. But, according to your requirements, you can increase or decrease this time interval.
If you want to increase this time interval then you need to set above 1 as follows:
If you want to decrease the interval then you will set the time less than 1 as follows:
Change ping packet size
Using the ping command, you can change the size of ping packets. The default size of the packet is set to 56 (84) bytes. The parentheses number represents that on sending ping bytes 28 packet header bytes will also include in the packet size. You can change this size using the following command:
The above command is used to test network performance.
For example, we have changed the ping packet size to 150 as follows:
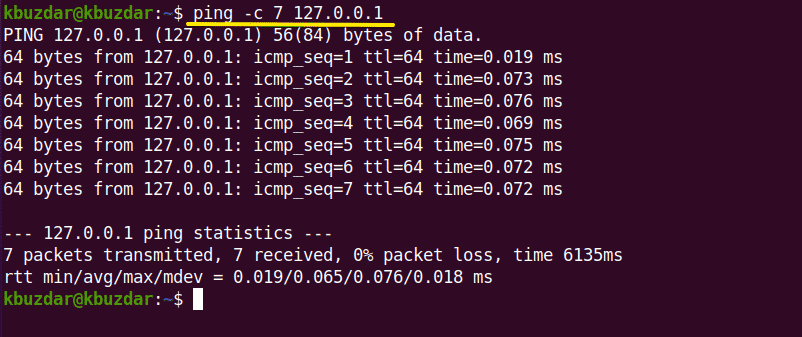
Set limit to desire number of ping packets
If you want to set limits that ping request automatically stopped after the specified number of ping packets then you can use the following command:
For example, set the ping request to 7 which means after sending 7 ping packets, the ping request will automatically terminate. You can see the output in the following image:
Using ping command flood a network
Under the heavy load, you can test your network performance using the ping flood. The ping flood must be executed under the root user. The ‘-f’ is used with ping command as follows:
Using this command, large packets send to the network for testing performance.
The dots represent the sending packet and it prints backspace for each response.
Set timeout for a ping request
Using the ping command, you can also set a timeout limit for ping requests. It means that after the specified time the ping will stop displaying the results on the terminal. Use the following command to check results:
Here, after 6 seconds ping automatically stops to print results.
Ping with an audible response
Using the following ping command, you can set a beep play that will check that the host available or not:
Check ping version
You can check the ping utility version using the following command:
In this article, we have practiced various ping command on Ubuntu 20.04 Linux system to check the network performance in an optimized way. Furthermore, you can work on advanced switches or tags that are used with ping command to customize the send and response requests.
from Linux Hint https://ift.tt/2YlzK8Q












0 Comments