Kubernetes, also known as k8s or simply as Kube, is an open-source container orchestration platform used for the automation scaling and deployment of containers. Minikube is a cross-platform and open-source tool that makes it possible for you to deploy a single-node Kubernetes cluster on your local machine or inside a virtual machine (vm). In this topic, you will learn how to install Kubernetes with Minikube on a CentOS 8 VM.
Prerequisites of MiniKube
- A copy of freshly installed CentOS 8 (with GUI) VM
- Minimum of 2 GB RAM and 2 vCPUs
- 20 GB hard disk space
- Root privileges
- A stable internet connection
With all the prerequisites met, it’s time now to roll up our sleeves and get our hands dirty.
Step 1) Install Updates and Disable SELinux
First and foremost, we are going to install the latest available updates necessary for the installation to proceed without any hitches. Run the following dnf command,
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# dnf update -y
Next, execute the commands below to disable SELinux,
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# setenforce 0 [root@minikube-centos8 ~]# sed -i --follow-symlinks 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/sysconfig/selinux
Step 2) Install Docker and Enable its Service
Since we are going to deploy a local Kubernetes cluster with MiniKube inside a VM. So, Install Docker CE on your CentOS 8 VM using the following commands,
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# dnf config-manager --add-repo=https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo Adding repo from: https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo [root@minikube-centos8 ~]# [root@minikube-centos8 ~]# dnf install docker-ce --nobest -y
Run following systemctl commands to start and enable docker service,
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# systemctl start docker [root@minikube-centos8 ~]# systemctl enable docker
Set the following firewall rules using firewall-cmd command,
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-masquerade --permanent [root@minikube-centos8 ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
Install “conntrack” package using following command, conntrack is the dependency for minikube setup,
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# dnf install conntrack -y
Note: Kubernetes using MiniKube can be installed on a local machine or server but for that it requires a hypervisor such as KVM or VirtualBox.
Step 3) Install Kubectl Manually
Kubectl is a command-line tool which interacts with Kubernetes cluster via APIs. Using kubectl we deploy our applications as deployment. By default, kubectl is not included in CentOS 8 package repositories. Therefore, we are going to manually install it using beneath commands,
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/`curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt`/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl [root@minikube-centos8 ~]# chmod +x ./kubectl [root@minikube-centos8 ~]# mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl [root@minikube-centos8 ~]# kubectl version --client
Output of above commands would be something like below,
Step 4) Install and Start Minikube
After installing the kubectl, let’s install minikube using the following commands,
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# curl -Lo minikube https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64 [root@minikube-centos8 ~]# chmod +x minikube [root@minikube-centos8 ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/bin/ [root@minikube-centos8 ~]# install minikube /usr/local/bin/
To start Minikube run the command:
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# minikube start --driver=none
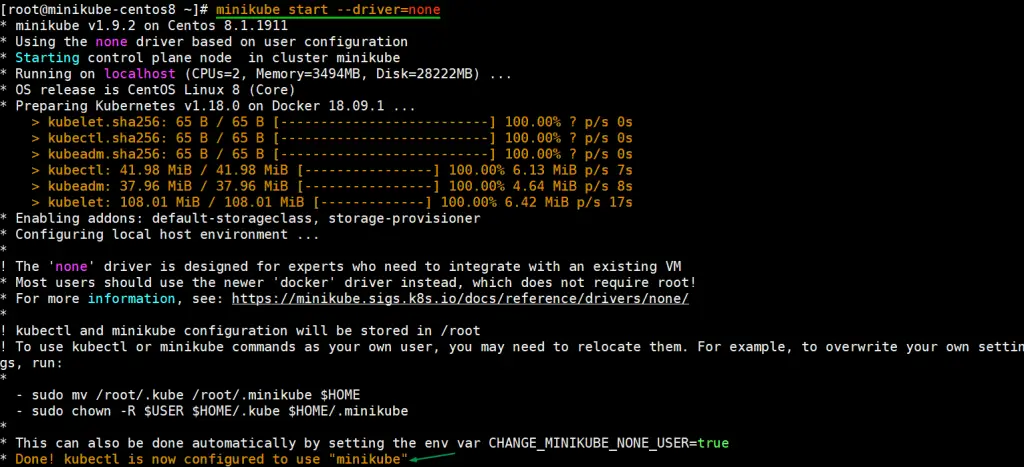
As we can see above output, minikube command has downloaded and started the docker containers for setting up single node Kubernetes cluster.
Run below minikube command to verify the status of your local Kubernetes cluster,
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# minikube status host: Running kubelet: Running apiserver: Running kubeconfig: Configured [root@minikube-centos8 ~]# minikube ip 192.168.29.216 [root@minikube-centos8 ~]#
To stop a Kubernetes cluster, execute,
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# minikube stop
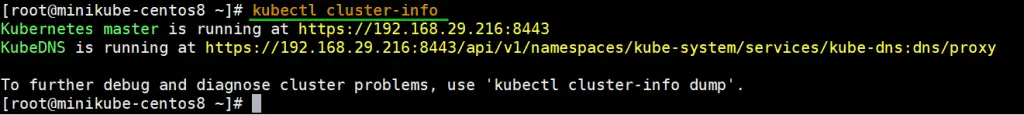
Execute the “kubectl cluster-info” command to view cluster information,
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# kubectl cluster-info
Run below command to view cluster nodes,
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION minikube-centos8 Ready master 144m v1.18.0 [root@minikube-centos8 ~]#
Step:6) Test and Verify Kubernetes Cluster
To test Kubernetes cluster, let try to create k8s deployment using echoserver image, it is equivalent to http web server and expose it as a service on port 8080,
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# kubectl create deployment test-minikube --image=k8s.gcr.io/echoserver:1.10 deployment.apps/test-minikube created [root@minikube-centos8 ~]#
To access test-minikube deployment, expose it as service, run the following command,
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# kubectl expose deployment test-minikube --type=NodePort --port=8080 service/test-minikube exposed [root@minikube-centos8 ~]#
Run below kubectl command to get pod information for above created deployment,
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# kubectl get pod NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE test-minikube-f4df69575-fkxdh 1/1 Running 0 3m29s [root@minikube-centos8 ~]#
To access service, get its url by running the beneath command.
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# minikube service test-minikube --url http://192.168.29.216:31356 [root@minikube-centos8 ~]#
Now type above url in your web browser,
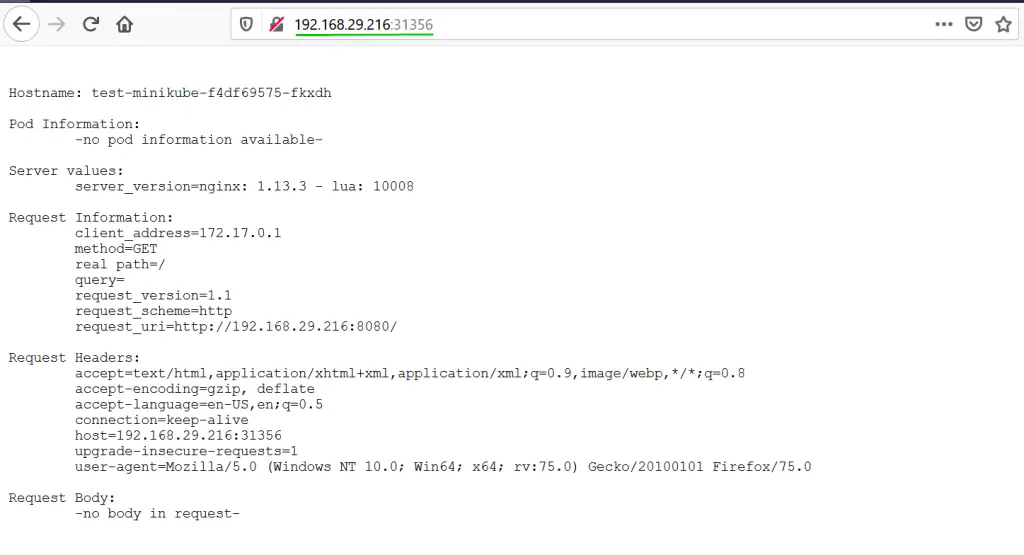
Great, it means our Kubernetes cluster is working fine. In the next step, let’s try to deploy and access Kubernetes dashboard
Step 7) Enable and Access Kubernetes Dashboard
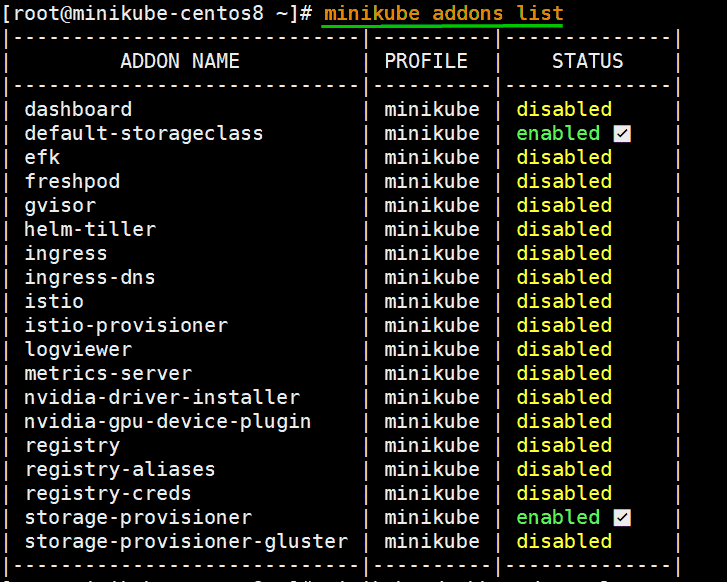
Kubernetes ships with a dashboard that allows you to manage your cluster. In Minikube, dashboard has been added as an addons.To view all the addons that come with minikube run:
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# minikube addons list
To activate the Kubernetes dashboard, execute below command,
[root@minikube-centos8 ~]# minikube dashboard --url
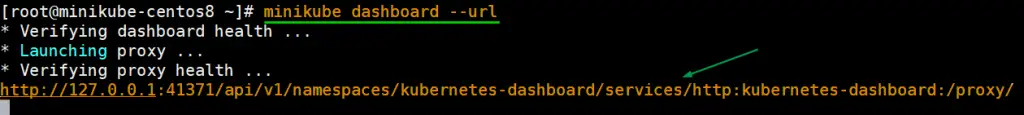
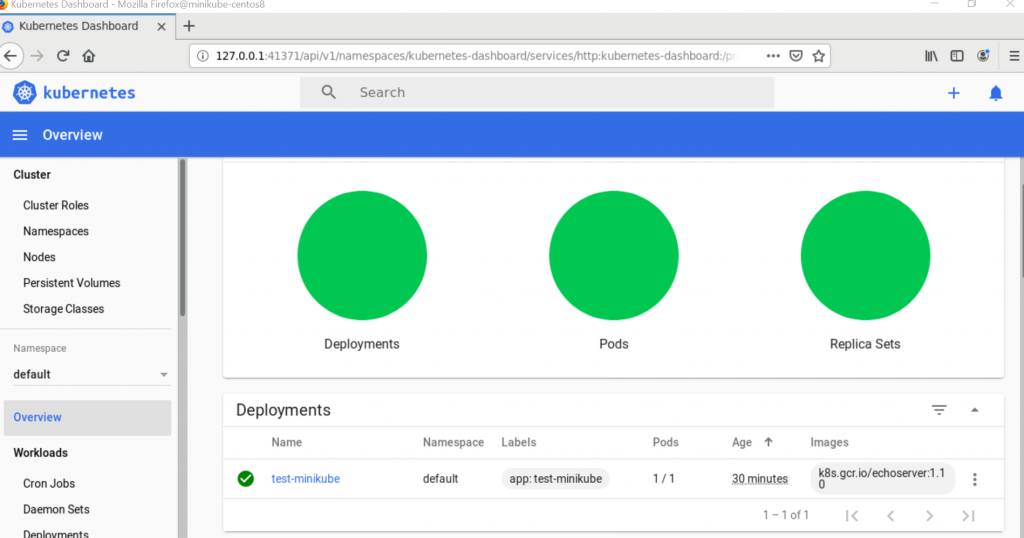
This will give us a dashboard url , copy and paste it on minikube system’s web browser.
And that’s just about it. We have managed to successfully install Kubernetes with Minikube on CentOS 8. You are welcome to share your feedback and comments.
from Linuxtechi https://ift.tt/2VjmcsK





0 Comments